
“When rocks impregnable are not so stout,
Nor gates of steel so strong, but time decays?” - Sonnet LXV.
堅牢な石壁も、鋼鉄の扉でさえも、時が朽ち果てさせてしまうだろうから…

□ AStarix: Fast and Optimal Sequence-to-Graph Alignment
>> https://www.biorxiv.org/content/10.1101/2020.01.22.915496v1.full.pdf
AStarix is a sequence-to-graph semi-global aligner based on A* shortest path algorithm. It supports general graphs and finds alignments that are optimal according to edit-distance with non-negative weights. AStarix parallelizes the alignment of a set of reads.
AStarix is consistently faster than Dijkstra, which is consistently faster than PaSGAL and GraphAligner.
Scaling AStarix may require a combination of the development of more clever heuristic functions and algorithmic optimizations. a (sub-optimal) seeding step could speed up AStarix by pre-filtering the starting positions, analogously to other optimal aligners.
□ UNCALLED: Targeted nanopore sequencing by real-time mapping of raw electrical signal
>> https://www.biorxiv.org/content/10.1101/2020.02.03.931923v1.full.pdf
UNCALLED, the Utility for Nanopore Current ALignment to Large Expanses of DNA, with the goal of mapping streaming raw signal to DNA references for targeted sequencing using ReadUntil.
UNCALLED probabilistically considers k-mers that the signal could represent, and then prunes the candidates based on the reference encoded within an FM-index.
UNCALLED also enriched 148 human genes associated with hereditary cancers to 29.6x coverage using one MinION flowcell, enabling accurate detection of SNPs, indels, structural variants, and methylation.
And also intend to add an optional dynamic time warping (DTW) step to UNCALLED, making it a full-scale signal-to-basepair aligner.

□ scTenifoldNet: a machine learning workflow for constructing and comparing transcriptome-wide gene regulatory networks from single-cell data
>> https://www.biorxiv.org/content/10.1101/2020.02.12.931469v1.full.pdf
The scTenifoldNet workflow combines principal component regression, low-rank tensor approximation, and manifold alignment.
scTenifoldNet constructs and compares transcriptome-wide single-cell GRNs (scGRNs) from different samples to identify gene expression signatures shifting with cellular activity changes such as pathophysiological processes and responses to environmental perturbations.
scTenifoldNet can be extended to adapt a non-random subsampling schema. the subsamples contain pseudotime information, and the multilayer scGRN constructed from these subsamples will contain the pseudotime trajectory information.

□ AERON: Transcript quantification and gene-fusion detection using long reads
>> https://www.biorxiv.org/content/10.1101/2020.01.27.921338v1.full.pdf
Recent long read RNA analysis methods such as TALON and Mandalorian rely on these alignment programs to align long mRNA sequences against a reference genome.
AERON is an alignment based pipeline for quantification and detection of gene-fusion events using only long RNA-reads. It uses a state-of-the-art sequence-to-graph aligner to align reads generated from long read sequencing technologies to a reference transcriptome.
Aeron uses GraphAligner, a fast sequence- to-graph alignment method, to align ONT reads to a reference transcriptome and find better alignments as compared to Minimap2, which is used as part of previous state-of-the-art quantification pipelines.
AERON makes use of a novel way to assign reads to transcripts, based on the position of the mapping of the read on the transcript and the fraction of the read contained in a transcript. AERON also introduces the first long read specific gene-fusion detection algorithm.
□ STELAR: a statistically consistent coalescent-based species tree estimation method by maximizing triplet consistency
>> https://bmcgenomics.biomedcentral.com/articles/10.1186/s12864-020-6519-y
STELAR (Species Tree Estimation by maximizing tripLet AgReement) is statistically consistent under the MSC model, fast (having a polynomial running time), and highly accurate – enabling genome wide phylogenomic analyses.
STELAR is an efficient dynamic programming based solution to the CTC problem which is highly accurate and scalable. STELAR matches the accuracy of ASTRAL and improves on MP-EST and SuperTriplets.
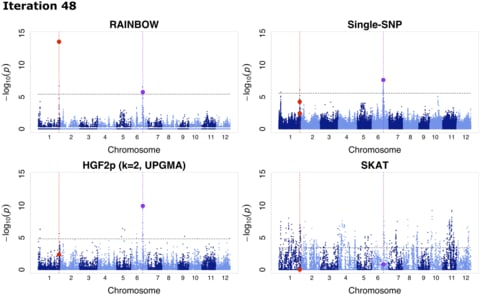
□ RAINBOW: Haplotype-based genome-wide association study using a novel SNP-set method
>> https://journals.plos.org/ploscompbiol/article?id=10.1371/journal.pcbi.1007663
RAINBOWR: Reliable Association INference By Optimizing Weights with R, a novel SNP-set GWAS approach, which is superior in controlling false positives and detecting rare variants compared with conventional approaches.
the application of RAINBOW to haplotype-based GWAS by regarding a haplotype block as a SNP-set, which enables one to perform haplotype-based GWAS without prior haplotype information.
RAINBOW detects the causal haplotype block with multiple causal variants. RAINBOW offers not only a SNP-set GWAS that can be applied to universal situations but also one that is faster with the restircted situations using linear kernel for constructing the Gram matrix of SNP-set.
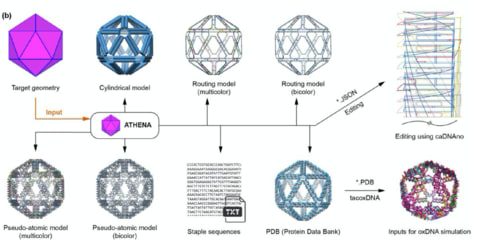
□ ATHENA: Rapid Prototyping of Wireframe Scaffolded DNA Origami
>> https://www.biorxiv.org/content/10.1101/2020.02.09.940320v1.full.pdf
ATHENA performs automated scaffold routing and staple sequence design, and generates the required staple strands needed to experimentally fold the structure.
ATHENA enables external editing of sequences using the caDNAno, asymmetric nanoscale positioning of gold nanoparticles, as well as atomic-level models for molecular dynamics, coarse-grained dynamics.
□ atomium — A Python structure parser
>> https://academic.oup.com/bioinformatics/advance-article/doi/10.1093/bioinformatics/btaa072/5733721
The atomium PDB parser can handle three of the principal file types of structural biology, save changes made to them, and generate the structures contained in their biological assembly instructions for more biologically realistic models.
there is a strong argument that atomium itself should not be extended to include features such as solvent accessibility calculation since these are outside the remit of parsing and representing macromolecular structure.
All structure classes can also use atomium’s filtering syntax. the atomic structures (a chain, a residue, a ligand etc.) can all be transformed geometrically by translating or rotating.
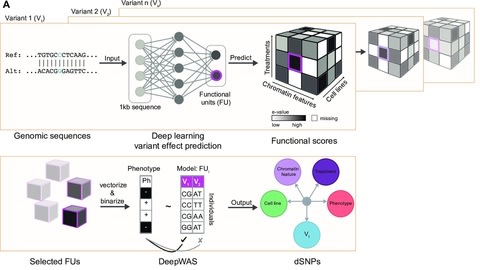
□ DeepWAS: Multivariate genotype-phenotype associations by directly integrating regulatory information using deep learning
>> https://journals.plos.org/ploscompbiol/article?id=10.1371/journal.pcbi.1007616
By integrating expression and methylation quantitative trait loci (eQTL and meQTL) information of multiple resources and tissues, DeepWAS identifies disease/trait-relevant transcriptionally active genomic loci.
DeepWAS might increase the power to detect true positive signals, by pre-selecting functionally relevant SNPs and integrating multivariate statistics.
DeepWAS identifies both known variants and highlights underlying molecular mechanisms. The DeepWAS approach identified SNP-phenotype associations directly in a cell type-specific regulatory context.
□ Sparse latent factor regression models for genome-wide and epigenome-wide association studies
>> https://www.biorxiv.org/content/10.1101/2020.02.07.938381v1.full.pdf
Computer simulations provided evidence that sparse latent factor regression models achieve higher statistical performance than other sparse methods, including the least absolute shrinkage and selection operator (LASSO) and a Bayesian sparse linear mixed model (BSLMM).
Additional simulations based on real data showed that sparse latent factor regression models were more robust to departure from the generative model than non-sparse approaches, such as surrogate variable analysis (SVA).
Sparse latent factor mixed models or sparse LFMM, a least-squares algorithm that jointly estimate effect sizes and confounding factors in sparse latent factor regression models.

□ PathExt: a general framework for path-based mining of omics-integrated biological networks
>> https://www.biorxiv.org/content/10.1101/2020.01.21.913418v1.full.pdf
PathExt is a computational tool, which, in contrast to differential genes, identifies differentially active paths when a control is available, and most active paths otherwise, in an omics-integrated biological network.
PathExt relies on two user defined parameters, the threshold k used to select the top k shortest paths, and the q-value for statistical significance of the paths selected to construct TopNet.
PathExt assigns weights to the interactions in the biological network as a function of the given omics data, thus transferring importance from individual genes to paths, and potentially capturing the way in which biological phenotypes emerge from interconnected processes.
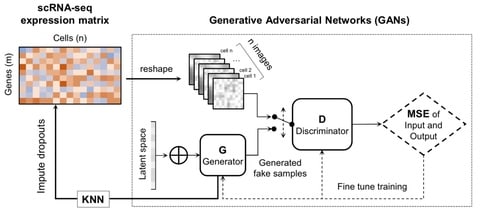
□ scIGANs: Single-cell RNA-seq Imputation using Generative Adversarial Networks
>> https://www.biorxiv.org/content/10.1101/2020.01.20.913384v1.full.pdf
The basic idea is that scIGANs can learn the non-linear gene-gene dependencies from complex, multi-cell type samples and train a generative model to generate realistic expression profiles of defined cell types.
ScIGANs is also compatible with other single-cell analysis methods since it does not change the dimension of the input data and it effectively recovers the dropouts without affecting the non-dropout expressions.
scIGANs is effective for dropout imputation and enhancing various downstream analysis. ScIGANs is also scalable and robust to small datasets that have few genes with low expression and/or cell-to-cell variance.
utilizing a time-course scRNA-seq data derived from the differentiation, and apply scIGANs and all other nine imputation methods to the raw scRNA-seq data with known time points and then reconstruct the trajectories.

□ MetaOmGraph: a workbench for interactive exploratory data analysis of large expression datasets
>> https://academic.oup.com/nar/advance-article/doi/10.1093/nar/gkz1209/5709708
MetaOmGraph overcomes the challenges posed by big size and complexity of big datasets by efficient handling of data files by using a combination of data indexing and buffering schemes.
MetaOmGraph can perform meta-analysis of Pearson correlations. By incorporating metadata, MetaOmGraph adds another dimension to the analyses and provides flexibility in data exploration.

□ Compressive Big Data Analytics: An Ensemble Meta-Algorithm for High-dimensional Multisource Datasets
>> https://www.biorxiv.org/content/10.1101/2020.01.20.912485v1.full.pdf
CBDA resembles various ensemble methods, like bagging and boosting algorithms, in its use of the core principle of stochastic sampling to enhance the model prediction. CBDA implements a two-phase bootstrapping strategy.
the scalability, efficiency and potential of CBDA to compress complex data into structural information leading to derived knowledge and translational action. CBDA employs SuperLearner as its ensemble predictor to combine into a blend of meta-learners.
□ ADT : A Generalized Algorithm and Program for Beyond Born-Oppenheimer Equations of 'N' Dimensional Sub-Hilbert Space
>> https://pubs.acs.org/doi/10.1021/acs.jctc.9b00948
The major bottleneck of first principle based beyond Born-Oppenheimer (BBO) treatment originates from large number and complicated expressions of adiabatic to diabatic transformation (ADT) equations for higher dimensional sub-Hilbert spaces.
a generalized algorithm, ADT to generate the nonadiabatic equations through symbolic manipulation and to construct highly accurate diabatic surfaces for molecular processes involving excited electronic states.
ADT program can be efficiently used to formulate analytic functional forms of differential equations for ADT angles and diabatic potential energy matrix; and solve the set of coupled differential equations numerically to evaluate ADT angles, residue due to singularity.

□ GraphSCI: Imputing Single-cell RNA-seq data by combining Graph Convolution and Autoencoder Neural Networks
>> https://www.biorxiv.org/content/10.1101/2020.02.05.935296v1.full.pdf
Graph convolution network exploits the spatial feature of gene-to-gene relationships effectively while Autoencoder neural network learns the non-linear relationships of cells and count structures of scRNA-seq data.
And the GraphSCI framework finally reconstructs gene expressions by integrating gene expressions and gene-to-gene relationships dynamically in the backward propagation of neural networks.

□ GENVISAGE: Rapid Identification of Discriminative and Explainable Feature Pairs for Genomic Analysis
>> https://www.biorxiv.org/content/10.1101/2020.02.05.935411v1.full.pdf
a suite of optimizations to make GENVISAGE more responsive and demonstrate that our optimizations lead to a 400X speedup over competitive baselines for multiple biological data sets.
With the carefully designed separability metric of GENVISAGE and its suite of sophisticated optimizations that accelerates evaluation, GENVISAGE is able to accurately return the highest ranking separating feature pairs for both datasets within two minutes on a single machine.
GENVISAGE relies on the Rocchio-based separability measure, and enables optimizations like TRANSFORMATION that can pre-compute important quantities from the feature-object matrix before the positive and negative object sets are even provided.

□ Joint Inference of Clonal Structure using Single-cell DNA-Seq and RNA-Seq data
>> https://www.biorxiv.org/content/10.1101/2020.02.04.934455v1.full.pdf
CCNMF – a new computational tool utilizing the Coupled-Clone Non-negative Matrix Factorization technique to jointly infer clonal structures in single-cell genomics and transcriptomics data.
The framework is based on optimizing an objective function that simultaneously maximizes clone structure coherence between single-cell gene expression matrix and CNV matrix, in which the two matrices are copuled by a dosage effect matrix linking expression to copy number.
The Coupled matrix can be estimated priorly either by a linear regression model using public paired RNA and DNA bulk sequencing data, or by using an uninformative prior as an identity matrix.
simulated cell-wise gene dropout events by randomly replacing fractions of the generated gene expression with zeros, such that Gij = 1ijX’ij mimicking a dropout effect 1ij ∼ Bernoulli(1/(1 + λi)).
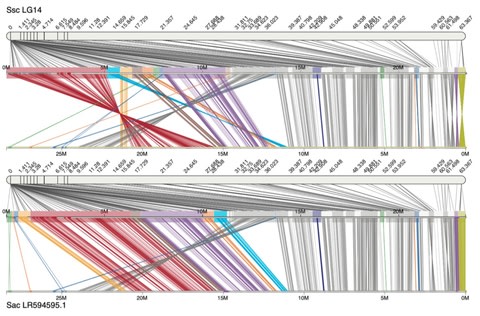
□ Chromonomer: a tool set for repairing and enhancing assembled genomes through integration of genetic maps and conserved synteny
>> https://www.biorxiv.org/content/10.1101/2020.02.04.934711v1.full.pdf
Chromonomer can create chromosome-level assemblies while providing extensive documentation of how the elements of evidence fit together.
For assemblies built from gapless, long-read contigs the basal Chromonomer algorithm could fail to correct misassemblies because incongruent marker orders have to be corrected by discarding markers within each contiguous sequence.
However, the markers that would be discarded include the very markers that delineate the intra-contig misassembly.
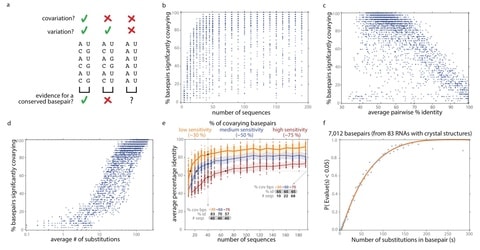
□ R-scape: Estimating the power of sequence covariation for detecting conserved RNA structure
>> https://academic.oup.com/bioinformatics/advance-article/doi/10.1093/bioinformatics/btaa080/5729989
a method for distinguishing when lack of covariation signal can be taken as evidence against a conserved RNA structure, as opposed to when a sequence alignment merely has insufficient variation to detect covariations.
Alignments for several long noncoding RNAs previously shown to lack covariation support do have adequate covariation detection power, providing additional evidence against their proposed conserved structures.
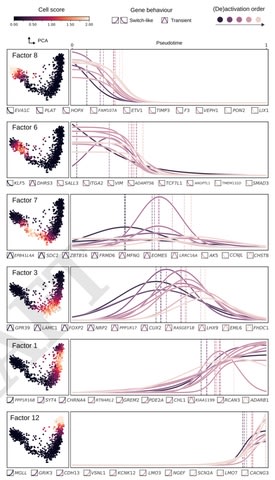
□ Untangling biological factors influencing trajectory inference from single cell data
>> https://www.biorxiv.org/content/10.1101/2020.02.11.942102v1.full.pdf
Confounding biological sources of variation can therefore perturb the inferred trajectory. by factorizing the matrix into distinct sources of variation, a relevant set of factors that constitute the core regulatory complexes can be selected for improving trajectory analysis.
focussing on the problem of pseudotime inference where the aim is to order developing cells along a "pseudotime" axis based on their transcriptional similarities.
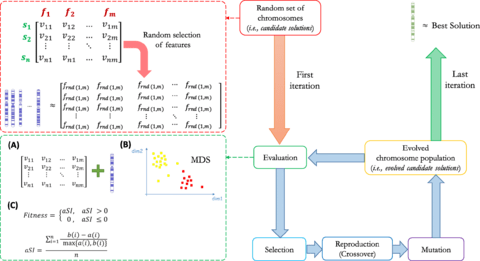
□ GARS: Genetic Algorithm for the identification of a Robust Subset of features in high-dimensional datasets
>> https://bmcbioinformatics.biomedcentral.com/articles/10.1186/s12859-020-3400-6
GARS may be applied on multi-class and high-dimensional datasets, ensuring high classification accuracy, like other GAs, taking a computational time comparable with basic FS algorithms.
By combining a dimension reduction method (i.e. MDS) with a score of similarity (i.e. silhouette index) between well-defined phenotypic sample groups (aka classes), GARS represents an innovative supervised GA implementation.
GARS is designed to solve a supervised problem where the averaged silhouette index calculation of the MDS result, and embedded in the fitness function to estimate how well the class-related phenotypes are grouped together while searching the optimal solution.
□ ZIAQ: A quantile regression method for differential expression analysis of single-cell RNA-seq data
>> https://academic.oup.com/bioinformatics/advance-article-abstract/doi/10.1093/bioinformatics/btaa098/5735412
a zero-inflation-adjusted quantile (ZIAQ) method, which is the first method to account for both dropout rates and complex scRNA-seq data distributions in the same model.
ZIAQ demonstrates superior performance over several existing methods on simulated scRNA-seq datasets by finding more differentially expressed genes.
□ scBatch: Batch Effect Correction of RNA-seq Data through Sample Distance Matrix Adjustment
>> https://academic.oup.com/bioinformatics/advance-article-abstract/doi/10.1093/bioinformatics/btaa097/5735411
scBatch, a numerical algorithm for batch effect correction on bulk and single cell RNA-seq data with emphasis on improving both clustering and gene differential expression analysis.
scBatch is not restricted by assumptions on the mechanism of batch effect generation. scBatch utilizes previous correction on sample distance matrices, such as QuantNorm, to further correct the count matrix.

□ Machine Boss: Rapid Prototyping of Bioinformatic Automata
>> https://www.biorxiv.org/content/10.1101/2020.02.13.945071v1.full.pdf
Machine Boss, a software tool implementing not just inference and parameter-fitting algorithms, but also a set of operations for manipulating and combining automata.
it is unnecessary to allocate storage for all 50 states during dynamic programming: the flanking context is always exactly determined by the position in the input genomic sequence, so only 5 states are ever accessible at any position in the dynamic programming matrix.
The interpretability is especially appealing when paths through the automaton have clear meaning—as is the case when state machines are used to represent biological processes such as translation and splicing, information-theoretic processes like radix-based coding.
Machine Boss includes a reference implementation of the Thorne-Kishino-Felsenstein model, and implements Matrix-like operations such as multiplication, transposition, addition, intersection, the matrix identity, and multiplication by a scalar.
□ seagull: lasso, group lasso and sparse-group lasso regularisation for linear regression models via proximal gradient descent
>> https://www.biorxiv.org/content/10.1101/2020.02.13.947473v1.full.pdf
seagull, a fast and numerically implementation via proximal gradient descent. The grid search for the penalty parameter is realised by warm starts. The step size between consecutive iterations is determined w/ backtracking line search, and produces complete regularisation paths.
In contrast to SGL, seagull computed the solution in a fraction of the time. seagull is a convenient envelope of lasso variants. seagull offers the opportunity to incorporate weights for each penalised variable which enables further variants of the lasso.
□ epiConv: Single-cell ATAC-seq clustering and differential analysis by convolution-based approach
>> https://www.biorxiv.org/content/10.1101/2020.02.13.947242v1.full.pdf
Based on the similarity matrix learned from epiConv, this algorithm to infer differentially accessible peaks directly from heterogeneous cell population to overcome the limitations of conventional differential analysis through two-group comparisons.
epiConv learns the similarities (or distances) between single cells from their raw Tn5 insertion profiles by a convolution-based approach, instead of a binary accessibility matrix.

□ MAC: Merging Assemblies by Using Adjacency Algebraic Model and Classification
>> https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fgene.2019.01396/full
For non-single paths, MAC extracts the adjacencies which are included in the path, then checks the classification of contigs where the adjacencies are located.
The identification of consensus blocks is to filter out the unreliable fragments caused by uneven sequencing depth and sequencing errors; the addition of classification is to optimize the adjacency algebraic model and eliminate the influence of repetitive regions.

□ GPU accelerated partial order multiple sequence alignment for long reads self-correction
>> https://www.biorxiv.org/content/10.1101/2020.02.14.946939v1.full.pdf
the CONSENT segmentation strategy based on k-mer chaining provides an optimal opportunity to exploit the parallel-processing power of GPUs.
This accelerated version of CONSENT provides a speedup for the whole error correction step that ranges from 1.95x to 8.5x depending on the input reads.
□ iSeqQC: a tool for expression-based quality control in RNA sequencing
>> https://bmcbioinformatics.biomedcentral.com/articles/10.1186/s12859-020-3399-8
iSeqQC implements various statistical approaches including unsupervised clustering, agglomerative hierarchical clustering and correlation coefficients to provide insight into outliers.
iSeqQC was designed to obtain comprehensive information on sample heterogeneity to detect outliers or cross-sample contamination in an expression-based sequencing experiment by implementing various statistical approaches including descriptive and dimensional reduction algorithms.
□ Analysis of variance when both input and output sets are high-dimensional
>> https://www.biorxiv.org/content/10.1101/2020.02.15.950949v1.full.pdf
two methods for generating a sequence of independent vectors in the linear span of the output layer: A Monte Carlo method (MC-ANOVA) which uses random vectors, and one based on eigenvectors (Eigen-ANOVA).
using simulations to assess the bias and variance of each of the methods, and to compare it with that of the Partial Least Squares (PLS)–an approach commonly used in multivariate-high-dimensional regressions.
□ readucks: Nanopore read de-multiplexer
>> https://github.com/artic-network/readucks
This package is inspired by the demultiplexing options in porechop but without the adapter trimming options - it just demuxes. It uses the parasail library to do pairwise alignment which provides a considerable speed up over the seqan library used by porechop due to its low-level use of vector processor instructions.

□ AS-Quant: Detection and Visualization of Alternative Splicing Events with RNA-seq Data
>> https://www.biorxiv.org/content/10.1101/2020.02.15.950287v1.full.pdf
AS-Quant efficiently handles large-scale alignment files with hundreds of millions of reads in different biological contexts and generates a comprehensive report for most, if not all, potential alternative splicing events, and generates high quality plots for the splicing events.
AS-Quant calculates the read coverage of the potential splicing exons and the corresponding gene, and categorize the splicing events into five different types based on annotation, and assess the significance of the events between two biological conditions.





















Fifty in addition to and even start dating sites repeatedly after the long long opening. various is still find it an overwhelming challenge if occassions are typically difficult to acquire this kind of age group ranges. n' it isn get started on searching for an internet adult relationship content using range dedicated to older person. buyer employ a policy so that there is no nervous about your own private facet cascading in a poor cards. Next bring in this stock portfolio with a photograph towards increased rank. it's simple to let other find you or that is available chnlove review your family editions and also by looking out the styles.
it is possible to styles of thousands of attractive single ladies, couples compared to fifty looking forward to you. Once you have opted a profile, phone a electronic nicely quick texting if for example woo is in fact virtual, invitation to experience a converse using a relevant video or a web cam. understanding that, method to start dating,to start a date which helps bring about chatter so it helps you become familiar with various other.
custom your first encounter in order to incorporate a common hobby, business which assists to determine a fast link near to which has often so this means when the two of you.
grow to be shrewd, be secure, and have an depart program. You are going out with somebody else you don be familiar with beautifully, So consider only public facilities and notice an expert you faith whom you dating exactly where there is you always be. If you start to have unsafe about almost anyone you by way of, well pass on.
via european union to positively AmericaThe Vikwearinggs posses landed ok.
To you have to be designated, they possess ended up with while in Heavener, oklahoma. We can merely predict as to the reasons the company arrived, but a majority archeologists are in agreement which will have been, to put it accurately, Vikwhilegs okla.
it has been confirmed regarding Vikings have actually discovered north american several times with our below. His untamed sit influenced further Vikings looking for this upcoming property. even close to being fifteen growth cycles daily, Leif Eriksson completely discovered new continent. for the following a long time, so many expeditions were enabled to the fresh solid ground, that the Norsemen acknowledged as "Vinland, Archeologists get widely discovered and tackled the Vikwheng townships while others Greenland america.
Once set living in Newfoundlor Nova Scotia, here courageous Vikings began to explore other places of this exceptional new world, new world ".
one could just think about the Norsemens hype given that they paddled these longboats south into your interesting locations, forgetting the cruel illnesses relating to freezing n,upper. their gets encompassing current day okla should have gave the look of a tremendous paradise poker, And could even be called is know for Idun, unquestionably the Norse goddess connected with springtime and furthermore immortal teens.
Rediscovery throughout the RunestoneIn a huge ravine in the middle of charmingdate scam air accepting jungles, each of our
Vikings assembled an incredible normal pillar.
this process pillar goes up from the soil such as a sentinel, drinking stored study
during these longstanding woods since way back when.
gauging 12 ft. tall, 10 feet across, furthermore 16 long,in plentiful, i would say the pillar
possesses number of created tokens commonly known as runes sincerely ripped to become the nation's face.
The Heavener Runestone stayed at tucked in covering the down
Ravine for years and years. all this was not
correct up until at 1838, in the event that thousands associated native americans are intentionally transferred off
tennessee throughout to northern oklahoma, that your particular runestone was first "was alerted to, the early Choctaws and also other settlers over.