私は、私が失ってきたもの、奪われてきたもの、逃れてきたもの、避けてきたもの、捨てたもの、忘れたもので出来ている。過ちから学び、けれど学ばれた教訓がカルマと釣り合う時は、終ぞ訪れない。

□ RefKA: A fast and efficient long-read genome assembly approach for large and complex genomes
>> https://www.biorxiv.org/content/10.1101/2020.04.17.035287v1.full.pdf
RefKA relies on breaking up a closely related reference genome into bins, aligning k-mers unique to each bin with PacBio reads, and then assembling each bin in parallel followed by a final bin-stitching step.
The assembly quality from RefKA is comparable with the assemblies produced by state-of-the-art assemblers, such as FALCON. RefKA reduces the computational requirements, by using unique k-mers, string graph and a tiling path.
□ Sparse multiple co-Inertia analysis with application to integrative analysis of multi -Omics data
>> https://bmcbioinformatics.biomedcentral.com/articles/10.1186/s12859-020-3455-4
smCIA method that imposes a sparsity penalty on mCIA loading vectors and structured sparse mCIA (ssmCIA) that employs a network-based penalty to incorporate biological information represented by a graph.
Ultra-high dimensionality is the inherited nature of -omics datasets, thus statistical models for analyzing -omics datasets benefit from feature selection procedure, and is able to select important pathways.

□ scLM: automatic detection of consensus gene clusters across multiple single-cell datasets
>> https://www.biorxiv.org/content/10.1101/2020.04.22.055822v1.full.pdf
The single-cell Latent-variable Model (scLM) uses the conditional negative binomial distribution with latent variables to disentangle co-expression patterns across multiple datasets.
The intrinsic biological variability of gene across all cells and all datasets is captured by the latent variables in a λ-dimension latent space.

□ COSMOS: Causal integration of multi-omics data with prior knowledge to generate mechanistic hypotheses
>> https://www.biorxiv.org/content/10.1101/2020.04.23.057893v1.full.pdf
COSMOS (Causal Oriented Search of Multi-Omics Space), combines extensive prior knowledge of signaling, metabolic, and gene regulatory networks with computational methods to estimate activities of transcription factors and kinases as well as network-level causal reasoning.
COSMOS uses CARNIVAL’s Integer Linear Programming optimization strategy to find the smallest coherent subnetwork causally connecting as many deregulated TFs. COSMOS can theoretically be used with any other additional inputs, as long as they can be linked to functional insights.
□ ICE: Predicting target genes of noncoding regulatory variants Predicting target genes of noncoding regulatory variants
>> https://academic.oup.com/bioinformatics/advance-article-abstract/doi/10.1093/bioinformatics/btaa254/5824790
ICE (Inference of Connected eQTLs) predict the regulatory targets of noncoding variants identified in studies of expression quantitative trait loci.
ICE achieves an area under the receiver operating characteristic curve (ROC-AUC) of 0.799 using random cross-validation, and 0.700 for a more stringent position-based cross-validation.
ICE assembles datasets using eQTL results from the Genotype-Tissue Expression (GTEx) project and learn to separate positive and negative pairs based on annotations characterizing the variant, gene and the intermediate sequence.

□ Analyzing Genomic Data Using Tensor-Based Orthogonal Polynomials
>> https://www.biorxiv.org/content/10.1101/2020.04.24.059279v1.full.pdf
a multivariate tensor-based orthogonal polynomial approach to characterize nucleotides or amino acids in a given DNA/RNA or protein sequence.
Given quantifiable phenotype data that corresponds to a biological sequence, this approach can construct orthogonal polynomials using sequence information and subsequently map phenotypes on to the polynomial space.
This analyses indicate that there exist substantial competing intramolecular interactions that can interfere with the intermolecular interaction between the STAR:target complex.

□ BioBombe: Compressing gene expression data using multiple latent space dimensionalities learns complementary biological representations
>> https://genomebiology.biomedcentral.com/articles/10.1186/s13059-020-02021-3
this multiple compression approach “BioBombe” after the large mechanical device developed by Alan Turing and other cryptologists in World War II to decode encrypted messages sent by Enigma machines.
BioBombe compresses gene expression input data using different latent dimensionalities and algorithms to enhance discovery of biological representations, and different biological features are best extracted by different models trained with different latent dimensionalities.

□ URnano: Nanopore basecalling from a perspective of instance segmentation
>> https://bmcbioinformatics.biomedcentral.com/articles/10.1186/s12859-020-3459-0
UR-net formulates the basecalling problem as a one-dimensional segmentation task. As in the post-process of URnano, consecutive identical masks are merged as one base, a region of consecutive identical masks is just an event segment.
Chiron uses CTC decoding to generate basecalls of variant length through beam-searching in the hidden unit space. URnano can be used as the basecaller in a re-squiggle algorithm, as it can do basecalling, event detection and sequence to signal assignment jointly.

□ SparkINFERNO: A scalable high-throughput pipeline for inferring molecular mechanisms of non-coding genetic variants
>> https://academic.oup.com/bioinformatics/advance-article/doi/10.1093/bioinformatics/btaa246/5824793
SparkINFERNO (Spark-based INFERence of the molecular mechanisms of NOn-coding genetic variants) prioritizes causal variants underlying GWAS association signals and reports relevant regulatory elements, tissue contexts, and plausible target genes they affect.
SparkINFERNO combines functional evidence from individual genomic analyses and produces a list of candidate variants, enhancer elements, and their target genes as supported by FANTOM5, Roadmap, GTEx, TF binding and other functional evidence.

□ IRIS: an accurate and efficient barcode calling tool for in situ sequencing
>> https://www.biorxiv.org/content/10.1101/2020.04.13.038901v1.full.pdf
IRIS (Information Recoding of In situ Sequencing) decodes image signals into nucleotide sequences along with quality and location information, and DAIBC (Data Analysis after ISS Base Calling) for interactive visualization of called results.
IRIS can also handle image data generated by other ISS technologies by adding the corresponding input parser modules. After minor modification of the input data structures, the following steps can be unified and barcode sequences and locations could be called automatedly.

□ Scalable hierarchical clustering by composition rank vector encoding and tree structure
>> https://www.biorxiv.org/content/10.1101/2020.04.12.038026v1.full.pdf
this algorithm to inspire a rich research field of encoding based clustering well beyond composition rank vector trees.
Consequently, it achieves linear time and space computational complexity hierarchical clustering, the algorithm is general and applicable to any high dimensional data with strong nonlinear correlations.

□ SICILIAN: Specific splice junction detection in single cells
>> https://www.biorxiv.org/content/10.1101/2020.04.14.041905v1.full.pdf
SICILIAN’s precise splice detection achieves high accuracy on simulated data, improves concordance between matched single-cell and bulk datasets, increases agreement between biological replicates, and reliably detects un-annotated splicing in single cells.
SICILIAN fits a penalized generalized linear model on the input RNA-seq data, where positive and negative training classes are defined based on whether each junctional read also has a genomic alignment.
SICILIAN increases the concordance between the detected junctions from 10x Chromium and bulk RNA-seq regardless of the pairs’ cells of origin, which is consistent with SICILIAN identifying and removing scRNA-seq specific artifacts.
□ The covariance shift (C-SHIFT) algorithm for normalizing biological data
>> https://www.biorxiv.org/content/10.1101/2020.04.13.038463v1.full.pdf
C-SHIFT algorithm uses optimization techniques together with the blessing of dimensionality philosophy and energy minimization hypothesis for covariance matrix recovery under additive noise.
C-SHIFT algorithm is specifically designed to recover the true empirical correlations. An alternative version of the C-SHIFT algorithm is based on trace minimization approach instead of energy minimization.

□ CNV-PG: a machine-learning framework for accurate copy number variation predicting and genotyping
>> https://www.biorxiv.org/content/10.1101/2020.04.13.039016v1.full.pdf
CNV-PG (CNV Predicting and Genotyping), can efficiently remove false positive CNVs from existing CNV discovery algorithms, and integrate CNVs from multiple CNV callers into a unified call set with high genotyping accuracy.
For CNV-G, a genotyper, which is compatible with existing CNV callers and generating a uniform set of high-confidence genotypes.

□ An Algorithm to Build a Multi-genome Reference
>> https://www.biorxiv.org/content/10.1101/2020.04.11.036871v1.full.pdf
the MGR algorithm, a global approach to create a string graph where the vertices are fragments of sequences while the edges present the order of the vertices on the genome.
By making the probability distribution of the next character depend on a longer context, MGR graph creates a higher order Markov Chain model.
the MGR algorithm that creates a graph as a multi-genome reference. To reduce the size and complexity of the multi-genome reference, highly similar orthologous and paralogous regions are collapsed while more substantial differences are retained.
□ Random Tanglegram Partitions (Random TaPas): An Alexandrian Approach to the Cophylogenetic Gordian Knot
>> https://academic.oup.com/sysbio/article-abstract/doi/10.1093/sysbio/syaa033/5820982
Random Tanglegram Partitions (Random TaPas) that applies a given global-fit method to random partial tanglegrams of a fixed size to identify the associations, terminals and nodes that maximize phylogenetic congruence.
with time-calibrated trees, Random TaPas is also efficient at distinguishing cospeciation from pseudocospeciation. Random TaPas can handle large tanglegrams in affordable computational time and incorporates phylogenetic uncertainty in the analyses.
the recursive partitioning of the tanglegram buffers the effect of phylogenetic nonindependence occurring in current global-fit methods and therefore Random TaPas is more reliable to identify host-symbiont associations that contribute most to cophylogenetic signal.

□ PathME: pathway based multi-modal sparse autoencoders for clustering of patient-level multi-omics data
>> https://bmcbioinformatics.biomedcentral.com/articles/10.1186/s12859-020-3465-2
The autoencoder based dimensionality reduction yields more statistically stable and coherent clusters, i.e. was successful in capturing relevant signal from the data.
PathME, a multi-modal sparse denoising autoencoder framework coupled with sparse non-negative matrix factorization to robustly that allows for an effective and interpretable combination of multi-omics data and pathway information.
□ yacrd and fpa: upstream tools for long-read genome assembly
>> https://academic.oup.com/bioinformatics/article-abstract/doi/10.1093/bioinformatics/btaa262/5823296
Filter Pairwise Alignment (fpa) takes as input pairwise align in the PAF or MHAP, and they can filter match by:
* type: containment, internal-match, dovetail
* length: match is upper or lower than a threshold
* read name: match against a regex, it's a read match against himself
Yet Another Chimeric Read Detector for long reads (yacrd) using all-against-all read mapping, and performes computation of pile-up coverage for each read, and detection of chimeras.
□ Sequoya: Multi-objective multiple sequence alignment in Python
>> https://academic.oup.com/bioinformatics/article-abstract/doi/10.1093/bioinformatics/btaa257/5823295
Sequoya is an open source software tool aimed at for solving Multiple Sequence Alignment problems with multi-objective metaheuristics. Sequoya offers a broad set of libraries for data analysis, visualisation, and parallelism.
□ AViS: Dataflow programming for the analysis of molecular dynamics
>> https://journals.plos.org/plosone/article?id=10.1371/journal.pone.0231714
By utilizing the dataflow programming (DFP) paradigm, algorithms can be defined by execution graphs, and arbitrary data can be transferred between nodes using visual connectors.
an Analysis and Visualization Software (AViS) application from scratch which utilizes the dataflow programming (DFP) paradigm and allows for graphical designing and debugging of algorithms.

□ Improving the coverage of credible sets in Bayesian genetic fine-mapping
>> https://journals.plos.org/ploscompbiol/article?id=10.1371/journal.pcbi.1007829
Bayesian genetic fine-mapping studies aim to identify the specific causal variants within GWAS loci responsible for each association, reporting credible sets of plausible causal variants, which are interpreted as containing the causal variant with some “coverage probability”.

□ More Accurate Transcript Assembly via Parameter Advising
>> https://www.liebertpub.com/doi/10.1089/cmb.2019.0286
quantifying the impact of parameter choice on transcript assembly and take some first steps toward generating a truly automated genomic analysis pipeline for automatically choosing input-specific parameter values for reference-based transcript assembly using the Scallop.

□ FastSK: Fast Sequence Analysis with Gapped String Kernels
>> https://www.biorxiv.org/content/10.1101/2020.04.21.053975v1.full.pdf
FastSK uses a simplified kernel formulation that decomposes the kernel calculation into a set of independent counting operations over the possible mismatch positions. This simplified decomposition allows us to devise a fast Monte Carlo approximation that rapidly converges.
FastSK matches or outperforms state-of-the-art string kernel methods, convolutional neural networks (CNN) and LSTM models in test performance across 10 DNA TFBS datasets.
□ A meta-learning approach for genomic survival analysis
>> https://www.biorxiv.org/content/10.1101/2020.04.21.053918v1.full.pdf
The performance of meta-learning can be explained by the learned learning algorithm at the meta-learning stage where the model learns from related tasks.
the meta-learning framework is able to achieve similar performance as learning from a significantly larger number of samples by using an efficient knowledge transfer.

□ BAMscale: quantification of next-generation sequencing peaks and generation of scaled coverage tracks
>> https://epigeneticsandchromatin.biomedcentral.com/articles/10.1186/s13072-020-00343-x
BAMscale accurately quantifies and normalizes identified peaks directly from BAM files, and creates coverage tracks for visualization in genome browsers.
BAMScale can be implemented for a wide set of methods for calculating coverage tracks, including ChIP-seq and ATAC-seq, as well as methods that currently require specialized, separate tools for analyses, such as splice-aware RNA-seq, END-seq and OK-seq.
□ scConsensus: combining supervised and unsupervised clustering for cell type identification in single-cell RNA sequencing data
>> https://www.biorxiv.org/content/10.1101/2020.04.22.056473v1.full.pdf
SCCONSENSUS, a computational strategy to find a consensus clustering that provides the best possible cell type separation for a single-cell data set.
Applying SCCONSENSUS, SEURAT and RCA to five CITE-seq data sets results suggests that RCA tends to find more clusters than SCCONSENSUS and SEURAT. On average SC-CONSENSUS leads to more clusters than SEURAT but to less clusters than RCA.
Any multidimensional single-cell assay whose cell clusters can be separated by differential features can leverage the functionality of scConsensus approach.
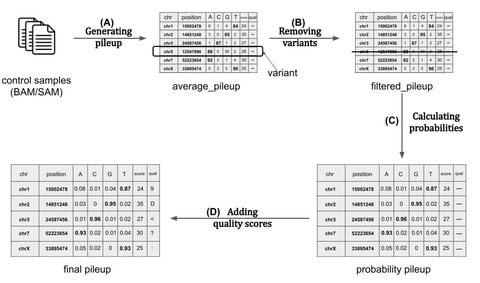
□ UMI-Gen: a UMI-based reads simulator for variant calling evaluation in paired-end sequencing NGS libraries
>> https://www.biorxiv.org/content/10.1101/2020.04.22.027532v1.full.pdf
UMI-Gen generates reference reads covering the targeted regions at a user customizable depth.
using a number of control files, it estimates the background error rate at each position and then modifies the generated reads to mimic real biological data.
□ Term Matrix: A novel Gene Ontology annotation quality control system based on ontology term co-annotation patterns
>> https://www.biorxiv.org/content/10.1101/2020.04.21.045195v1.full.pdf
the inspection of annotations co-annotated to multiple processes can identify annotation outliers, systematic mapping errors, and ontology problems for validation or correction.
widely propagated annotation errors affect common uses of GO data; for example, misannotation of many genes to the same term in a given species can obscure enrichments.
Term Matrix builts a co-annotation QC into GO procedures, thereby enabling curators to distinguish between new annotations that provide additional support for known biology and those that reflect novel, previously unreported connections between divergent processes.

□ Co-expression analysis reveals interpretable gene modules controlled by trans-acting genetic variants
>> https://www.biorxiv.org/content/10.1101/2020.04.22.055335v1.full.pdf
a rare detailed characterisation of a trans-eQTL effect cascade from a proximal cis effect to the affected signalling pathway, transcription factor, and target genes.
combinng all credible sets into an undirected graph where every node represents a credible set of a module from a triplet and defined an edge between two nodes if the corresponding credible sets shared at least one overlapping variant.
□ Universality of cell differentiation trajectories revealed by a reconstruction of transcriptional uncertainty landscapes from single-cell transcriptomic data
>> https://www.biorxiv.org/content/10.1101/2020.04.23.056069v1.full.pdf
transcriptional uncertainty landscape, based on the cell likelihood value from CALISTA analysis to characterize the stochastic dynamics of the gene transcription process during cell differentiation.
The stochastic gene transcriptional model enabled identifying the specific parameters or mechanisms that explain the observed changes in the the gene transcriptional uncertainty at the single-cell level.

□ SSEMQ: Joint eQTL mapping and Inference of Gene Regulatory Network Improves Power of Detecting both cis- and trans-eQTLs
>> https://www.biorxiv.org/content/10.1101/2020.04.23.058735v1.full.pdf
the structure equation model (SEM) to model both GRN and effect of eQTLs on gene expression, and then develop a novel algorithm, named sparse SEM, for eQTL mapping (SSEMQ) to conduct joint eQTL mapping and GRN inference.
□ MaxHiC: robust estimation of chromatin interaction frequency in Hi-C and capture Hi-C experiments
>> https://www.biorxiv.org/content/10.1101/2020.04.23.056226v1.full.pdf
MaxHiC, a background correction tool that deals with these complex biases and robustly identifies statistically significant interactions in both Hi-C and capture Hi- C experiments.
MaxHiC uses a negative binomial distribution model and a maximum likelihood technique to correct biases in both Hi-C and capture Hi-C libraries.
In MaxHiC, distance is modelled by a function that decreases at increasing genomic distances to reach a small but constant non-zero value to account for random ligations.

□ SQMtools: automated processing and visual analysis of 'omics data with R and anvi'o
>> https://www.biorxiv.org/content/10.1101/2020.04.23.057133v1.full.pdf
SQMtools relies on the SqueezeMeta software for the automated processing of raw reads into annotated contigs and reconstructed genomes.
This engine allows users to input complex queries for selecting the contigs to be displayed based on their taxonomy, functional annotation and abundance across the different samples.
□ Stochastic approach optimizes a system’s wavefunction to improve computational efficiency: Multireference configuration interaction and perturbation theory without reduced density matrices
>> https://aip.scitation.org/doi/full/10.1063/10.0001200
By breaking apart a large computation into smaller components, researchers can solve the Schrodinger equation for complicated systems.
“These wavefunctions happen to be at just the right level of difficulty that, although it is possible to perform polynomial-scaling deterministic calculations with them, the cost scales quite unfavorably with the size of the active space.”

□ Eliciting priors and relaxing the single causal variant assumption in colocalisation analyses
>> https://journals.plos.org/plosgenetics/article?id=10.1371/journal.pgen.1008720
Horizontal integration of summary statistics from different GWAS traits can be used to evaluate evidence for their shared genetic causality.
the prior probability of colocalisation may depend on the trait pairs under consideration, evaluating the effect of mis-specifying prior parameters and/or not conditioning when multiple causal variants exist.

□ BD5: an open HDF5-based data format to represent quantitative biological dynamics data
>> https://www.biorxiv.org/content/10.1101/2020.04.26.062976v1.full.pdf
Biological Dynamics Markup Language (BDML) is an XML(Extensible Markup Language)-based open format that is also used to represent such data; however, it becomes difficult to access quantitative data in BDML files when the file size is large.
It can be used for representing quantitative biological dynamics data obtained from bioimage informatics and mechanobiological simulations.
□ aPCoA: Covariate Adjusted Principal Coordinates Analysis
>> https://academic.oup.com/bioinformatics/advance-article-abstract/doi/10.1093/bioinformatics/btaa276/5825727
Given a non-Euclidean pairwise distance matrix, principal coordinates analysis, also known as classic or metric multidimensional scaling, can allow to visualize variation across samples and potentially identify clusters by projecting the observations into a lower dimension.
aPCoA allows for the adjustment of one covariate, which can be either continuous or categorical, & provides options for visualization incl the plotting of 95% confidence ellipses & lines linking cluster members to the cluster center, & enables adjustment for multiple covariates.

The Nebula model, eliminates personal genomics companies as middlemen between data owners and data buyers. Nebula Genomics has established a partnership with Enigma.

Enigma: Decentralized Computation Platform with Guaranteed Privacy

Genomic data that was not generated at Nebula sequencing facilities can be offered on the Nebula network as well. This includes personal genomic data as well as data from non-profit (8D) and for-profit (8E) genomic databanks.