□ Ted Pim: Street Artist Revamps Abandoned Buildings With Creepy Baroque Imagery:
>> http://www.huffingtonpost.com/entry/street-artist-revamps-abandoned-buildings-with-baroque-imagery_55a68bb3e4b0c5f0322bff12
学び、気付き、死ね。私が生きている間に深層心理に潜り込み、得た智慧や知見は、その表現の手前で大部分が失われて、誰にも伝わることがなく、誰かにとって価値のあるものではない。共感という気休めの儀式だけが遺る。
心というのは浸食過程だ。一刻一刻と寄せて返す水流の、壁を打って翻る渦のようなもの。次の瞬間には泡に消えて、削られた岸へ岸へと推し進むだけ。
私たちに時間は残されていない。灰燼だけが安らぎの在り処だ。そして思考と因果の座すところは地と星ほどに離れている。
人は人との繋がりによって学ぶのではないと感じる。他己の瞳の宿す光は、己のそれと光源を同じくして、内側から辺縁に投影されるパルスに似る。私たちが見ているのは誰かではなく、誰かに為り替わる影であり、彼我の狭間に移ろうように見えるだけ。知り得ることは伝わるのではなく、洞察するのである。
何かを概念化するということは、何かの概念化をしないということである。計算可能なセグメントは制限されているから、何かのカードをめくれば、何処かのカードが翻る。そのすべてを開示することは出来ないかもしれない。我々が何かを理解するという事象は、何かについてのスタンスを得ることに等しい。

□ Deep Genomics: a start-up bringing the power of deep learning to genomics:
>> http://www.deepgenomics.com
Deep Genomics's SPIDEX is produced state-of-the-art splicing simulator assembled by our proprietary deep learning algorithms. It captures 65% of variance of splicing levels across exon triplets observed to undergo alternative cassette splicing. It is a Bayesian ensemble of DNN trained w/ RNA-seq data from a diverse set of healthy human tissues & thousands of engineered RNA features.

□ DeepBind: Predicting the sequence specificities of DNA/RNA binding proteins by Deep Learning:
>> http://www.nature.com/nbt/journal/vaop/ncurrent/full/nbt.3300.html
DeepBind computes a binding score f(s) using four stages:
f(s) = netW(pool)(rect b(convM(s))))
The convolve, rectify, pool and neural network stages predict a separate score for each sequence using the current model parameters.

(Cram ́er-von Mises test sensitivity to changes in parameters of the Poisson-Beta distribution.)
□ Discrete Distributional Differential Expression (D3E) A Tool for Gene Expression Analysis of Single-cell RNA-seq Data
>> http://biorxiv.org/content/early/2015/07/25/020735
D3E is based on an analytically tractable stochastic model, and thus it provides additional biological insights by quantifying biologically meaningful properties, , such as the average burst size and frequency.
□ BayesPI-BAR: a new biophysical model for characterization of regulatory sequence variations:
>> http://nar.oxfordjournals.org/content/early/2015/07/21/nar.gkv733.full
the chemical potential is protein-specific in the biophysical modeling of TF–DNA interaction it affects the in silico computation of TF binding affinity changes (i.e. δdbA)

□ The Human Phenotype Ontology: Semantic Unification of Common and Rare Disease:
>> http://www.cell.com/ajhg/abstract/S0002-9297(15)00234-7
HPO applied a phenotype-aware CR system (the Bio-LarK Concept Recognizer) with 5,136,645 of 22,376,811 articles listed in PubMed. CR & Bioinformatic Analysis: Validation w/ OMIM, Orphanet & DO assessing phenotype sharing, linked to the same locus
□ GAML: genome assembly by maximum likelihood w/ systematic combination of diverse seq-data into a single assembly:
> http://www.almob.org/content/10/1/18
GAML can use any combination of insert sizes w/ Illumina, 454 & PacBio in a encompaasing error rate, comparable to ALLPATHS-LG or Cerulean.
compute the final score as a weighted combination of log average probabilities
LAP(A|R1,…,Rk)=w1LAP(A|R1)+…+wkLAP(A|Rk).
□ ASTRID: Accurate Species TRees from Internode Distances: statistically consistent under the MSC, faster than ASTRAL-2
>> http://biorxiv.org/content/biorxiv/early/2015/07/22/023036.full.pdf
ASTRID will be most useful as a starting tree for use within more computationally intensive analyses, including Bayesian MCMC analyses (e.g., *BEAST) or maximum likelihood analyses.
The input to ASTRID is a set of unrooted gene trees T1,...,Tk.WeletSi =L(Ti) denote the leafset of Ti, and S = ∪iL(Ti). Let |S| = n.
under the assumption that k > n and that ASTRID uses a distance-based method that runs in O(n^3) time, ASTRID’s running time is O(kn^2).

□ Knowledge transfer via classification rules using functional mapping for integrative modeling of gene expression data
>> http://www.biomedcentral.com/1471-2105/16/226
Ganchev and colleagues proposed a novel framework ― transfer rule learning (TRL) which leverages the concept of transfer learning to build an integrative model of classification rules from two datasets.
using semantic similarity as a distance measure, construct a similarity matrix among the GO terms. with the similarity matrix as input, applied the spectral clustering algorithm to group the GO terms into functionally similar clusters. TRL-FM can facilitate knowledge transfer among MAGE datasets that have different variable symbols, as long as the variables can be mapped to a common biological functions.

□ Red: an intelligent, rapid, accurate tool for detecting repeats de-novo on the genomic scale
>> http://www.biomedcentral.com/1471-2105/16/227
Red is designed using Signal Processing & Machine Learning as well as a novel data structure to handle long DNA sequences efficiently. Red is the first repeat-detection tool that has the capability of labeling own training data and train itself automatically on each genome. A state in the Hidden Markov Model is designed to generate a specific range of scores that have the same logarithmic value.
□ RUVSeq: How data analysis affects power, reproducibility & biological insight of RNA-seq studies in complex datasets
>> http://nar.oxfordjournals.org/content/early/2015/07/21/nar.gkv736.full
RUV considerably increases the number of genes discovered as differentially expressed. RUV considerably increases the number of genes discovered as differentially expressed. indeed an improvement in the detection of true biological signal by showing that it increases the discovery of positive controls, known pathways involved in learning and memory and cross-platform concordance.
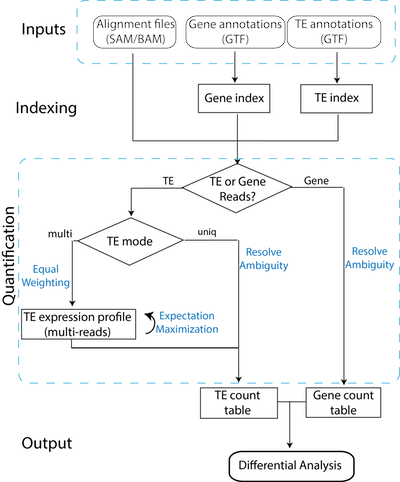
□ TEtranscripts: A package for including transposable elements in differential expression analysis of RNA-seq datasets:
>> http://bioinformatics.oxfordjournals.org/content/early/2015/07/22/bioinformatics.btv422.short
TETranscripts quantifies both gene and transposable element (TE) transcript abundances from RNA-Seq, utilizing both uniquely and ambiguously mapped short read sequences. It processes the short reads alignments (BAM files) and proportionally assigns read counts, to the corresponding gene or TE based on the user-provided annotation files (GTF files)
□ MetaFast: fast reference-free graph-based comparison of shotgun metagenomic data:
>> http://mccmb.belozersky.msu.ru/2015/proceedings/abstracts/37.pdf
Calculating a characteristic vector for every metagenome with a length equal to the number of connected components. Each vector element is the number of k-mers from a connected component that are present in reads of the metagenome. Cross-comparing metagenomes by calculating the Bray-Curtis dissimilarity matrix based on characteristic vectors.
□ Genomic Contextual Data JSON:
>> http://gensc.org/projects/gcdj/
The GCDJ core component supersedes Genomic Contextual Data Markup Language (GCDML) and adds a framework of tools.The GSC has groomed the MIxS standard into a stable, productive state and new standards are being constantly developed (e.g. MIBiG, MSB3). The INSDC and large analysis pipelines (e.g. MG-RAST) accepts and validates MIxS-compliant metadata.
□ For Reproducible bioinformatics research.
・ When Analyses that include randomness, Note underlying random seeds.
・Generate hierarchical Analysis output, allowing Layers of increasing Detail to be Inspected.
・Connect textual statements to Underlying Results, and provide Public Access to Scripts, Runs, and Results.
□ Renormalized spacetime is two-dimensional at the Planck scale:
>> http://arxiv.org/pdf/1507.05669.pdf
a physical ansatz to relate the renormalized metric tensor to the bare metric tensor such that the spacetime acquires a zero-point length l0 of the order of the Planck length LP.
the Euclidean volume VD(l,l0) in a D-dimensional spacetime of a region of size l scales as VD(l,l0) ∝ lD-2l2 0 when l ∼ l0 , while it reduces to the standard result VD (l, l0 ) ∝ lD at large scales (l ≫ l0). The appropriately defined effective dimension, Deff, decreases continuously from Deff = D (at l ≫ l0) to Deff = 2 (at l ∼ l0).
the existence of the zero-point-length in the spacetime and leads to well defined computation rules which can incorporate the effects of quantum gravity at mesoscopic scales w/o us leaving the comfort of a continuum differential geometry.

(The non-backtracking (NB) matrix and weak nodes. The optimal strategy for immunization and spreading minimizes λ by removing the minimum number of nodes that destroys all the loops.)
□ Influence maximization in complex networks through optimal percolation:
>> http://www.nature.com/nature/journal/vaop/ncurrent/abs/nature14604.html
map the problem onto optimal percolation in random networks to identify the minimal set of influencers, which arises by minimizing the energy of a many-body system, where the form of the interactions is fixed by the non-backtracking matrix.
□ CN-Summ: Complex Networks and Extractive Summarization
>> https://www.inf.pucrs.br/~propor2010/proceedings/phdmsc/AntiqueiraNunes.pdf
k-core strategyに関する記述が余りにも少ないので他の論文を当たって見た。単純にk-coreを用いた集計手順か.
A subgraph g of a graph G is a k-core if every node i of g has degree at least equal to k. This subgraph must also be the greatest subgraph of G that has this property. Notice that a non empty k-core w/ the maximum possible k called the innermost k-core, is a subgraph that consists of densely connected nodes.
□ Testbeds and Research Infrastructure: Development of Networks and Communities:
>> https://books.google.co.jp/books?id=JGC7BQAAQBAJ
In other words, k-core strategy selects a group of nodes that have minimum degree among themselves, each selected node has a degree higher than or equal to k within the wormhole. In order to find the Core wormhole the algorithm described above in the k-Core strategy is executed on a binary search for the largest k that returns a non-empty set of nodes.
□ Ibis: Scaling the Python Data Experience: a new data analysis framework launched today:
>> http://www.ibis-project.org
Ibis enable Python to become a true first-class language for Apache Hadoop, without compromises in functionality, usability, or performance. Ibis expands the useful set of Python that can be translated to LLVM IR to achieve true native performance at scale on complex data w Impala and exposing machine learning functionality already available in MADLib.
□ morgantaschuk: Biologists and bioinformaticians have different software needs
>> https://modernmodelorganism.wordpress.com/2015/07/19/biologists-and-bioinformaticians-have-different-software-needs
Computational biologists are interested in results and Bioinformaticians are interested in methods.
As many bioinformatics tools can easily be statically linked,it's not too hard to keep binaries working even if you update the basic system. at the moment it feels like there's about a dozen workflow management systems (WMS), all having a different focus, different priorities and different ways to define your pipeline. The "common workflow language" was started at BOSC 2014 to solve this.
□ Alignment of time course gene expression data and the classification of developmentally driven genes with HMM:
>> http://www.biomedcentral.com/1471-2105/16/196
Interpolation of the expression values between observed time points is not readily justified as significant non-linear variations in expression could conceivably occur between adjacent time points.
□ do_x3dna: a tool to analyze structural fluctuations of dsDNA or dsRNA from molecular dynamics simulations:
>> http://bioinformatics.oxfordjournals.org/content/31/15/2583.short
a Python module dnaMD to perform and visualize statistical analyses of complex data obtained from the trajectories.
□ HAlign: Fast multiple similar DNA/RNA sequence alignment based on the centre star strategy:
>> http://bioinformatics.oxfordjournals.org/content/31/15/2475.short
□ Randomized embeddings for Extreme Learning: SVD of a particular matrix: randomized approximations to kernel machines
>> https://github.com/pmineiro/randembed
Given features X and labels Y, where the SVD of X is given by
X = UX ΣX VX
and the SVD of (UXT Y) is
UXT Y = UE ΣE VE,
the k-dimensional embedding is defined as the first k columns of VE. This definition is motivated by the optimal rank-constrained least-squares approximation of Y given X. Randomized methods provide a fast way of approximating these SVDs when the dimensionalities are large.
□ Fast Label Embeddings via Randomized Linear Algebra:
>> http://arxiv.org/abs/1412.6547
The result is a randomized algorithm whose running time is exponentially faster than naive algorithms. on two large-scale public datasets, from the Large Scale Hierarchical Text Challenge and the Open Directory Project. embeddings can be part of a strategy for zero-shot learning, i.e., designing a classifier which is extensible in the output space.

□ Python Machine Learning: Unlock deeper insights into cutting-edge predictive analytics
>> https://www.packtpub.com/big-data-and-business-intelligence/python-machine-learning
□ Sealer: a scalable gap-closing application for finishing draft genomes:
>> http://www.biomedcentral.com/1471-2105/16/230
sealer uses the succinct Bloom filter representation of a de Bruijn graph to close gaps in draft assemblies, incl very large genomes. it scales to successfully close 50.8 % and 13.8 % of gaps in human (3 Gbp) and white spruce (20 Gbp) draft assemblies in under 30 and 27 h,
□ Illumina Inc (ILMN) Discloses Files Form 4 Insider Selling : Christian O Henry Sells 5,390 Shares:
>> http://www.insidertradingreport.org/illumina-inc-ilmn-files-form-4-insider-selling-christian-o-henry-sells-5390-shares/642423/
Currently the company Insiders own 1.4% of Illumina Inc. In the past 6 months, there is a change of -26.38% in the total insider ownership. Illumina Inc sold 5,390 shares. The Insider selling transaction was disclosed on Jul 17, 2015 to the Securities and Exchange Commission. The shares were sold at $229.73 per share for a total value of $1,237,613.00.
□ Alexandria Real Estate Equities PT Lowered to $97.00 (ARE):
>> http://www.dakotafinancialnews.com/alexandria-real-estate-equities-pt-lowered-to-97-00-are/264805/
In other Alexandria Real Estate Equities news, CIO Peter M. Moglia sold 2,666 shares of the company’s stock in a transaction dated June 29. The stock was sold at an average price of $88.25, for a total transaction of $235,274.50.

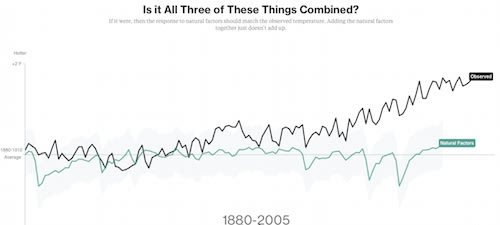
近年の地球温暖化「否定論」が、いかに観測データを無視してるかを示す簡潔なシミュレーション。温室効果ガス要因だけで温暖化モデルの要素を満たしてる。太陽活動も寄与していない。極端な環境からデータ採取することの妥当性も。
□ omgirlsvt
Climate deniers blame #globalwarming on nature. This NASA data begs to differ http://www.bloomberg.com/graphics/2015-whats-warming-the-world/ … #climatechange
Climate scientists tend not to report climate results in whole temperatures. Instead, they talk about how the annual temperature departs from an average, or baseline. They call these departures "anomalies."
□ The Brain vs Deep Learning: Computational Complexity or Why the Singularity Is Nowhere Near
>> https://timdettmers.wordpress.com/2015/07/27/brain-vs-deep-learning-singularity/
an extended linear-nonlinear-Poisson cascade model as groundwork and related it to convolutional architectures.
アナロジーが複雑系に対する相似構造の投影だとしたら、自明性は全て計量できるはずだ。私たちにはリソースが与えられていないだけなのか。
The brain represents object categories w/in a continuous semantic space which is organized into broad gradients across the cortical surface. This semantic space is shared across different individuals, underlying category representation in the brain probably has many dimensions.