
□ 言語にはアプリオリな構造性があると強く思わせられるが、言葉の指向性については、おそらく私は信じてはいない。然し、言葉がどのように偽り、何を隠そうとするのかについては、生涯をくべて惹きつけられている。
□ 要素間の動態から導かれる規則性を因果や相関と関係付けがちだが、それが出自の無関係な要素の『投影』であるとは、とかく信じがたいものである。

□ Four-dimensional coherent electronic Raman spectroscopy:
>> http://aip.scitation.org/doi/full/10.1063/1.4979485
GRadient-Assisted Multi-dimensional Electronic Raman Spectroscopy (GAMERS), the combined use of resonant and non-resonant excitation. This provides access to a wide variety of interactions in complex molecular systems from semi-conductors to DNA. In total, the pulse sequence creates a pair of zero-quantum coherences (ZQCs) and a pair of single-quantum coherences (SQCs).
□ Nanopore sequencing and assembly of a human genome with ultra-long reads:
>> http://biorxiv.org/content/biorxiv/early/2017/04/20/128835.full.pdf …
an additional 5×-coverage of ‘ultra-long’ reads (read N50 of 99.7kb) more than doubled the assembly contiguity. that platform throughput continues to improve, with individual flowcells generating >5 Gb of data at best, representing about 12.5% of the theoretical capacity of a 100% efficient flowcell running at 450 bases/second for 48 hours. The signalAlign algorithm uses a variable order hidden Markov model combined with a hierarchical Dirichlet process (HMM-HDP) to infer base modifications in a reference sequence using the ionic current signal produced by nanopore sequencing.

□ Refactoring the Genetic Code for Increased Evolvability:
>> http://biorxiv.org/content/biorxiv/early/2017/04/17/128058.full.pdf
explore several possible genetic codes that allow a greater degree of accessibility to the mutational landscape and may result in a hyper-evolvable organism serving as an ideal platform for directed evolution experiments.
Codon reassignments can also be penalized by reducing F using a factor alpha^N, where N = 1 for linear penalties and N = 2 for square penalties, resulting in the Change Minimizing Code (CMC) and CMC^2, respectively.
F_{unique} = num(AA(C’_{i}) where D(C, C’_{i}) = 1) / N
F_{ratio}=min( _{j}^{N}ifAA(C=>C’)==A_{i}1else0)/max(..)fori={0,M}
F_{chem} = num(CHEM_CLASS(AA(C’_{i})) where D(C, C’_{i}) = 1)/N
F = F_{unique}/F_{unique, max}*F_{ratio}/F_{ratio,max}*F_{chem}/F_{chem,max}

□ Genomics reboots deep learning:
>> https://www.ebi.ac.uk/about/news/press-releases/deep-learning-epigenetics

□ ChimeRScope: a novel alignment-free algorithm for fusion transcript prediction using paired-end RNA-Seq data:
>> https://academic.oup.com/nar/article-lookup/doi/10.1093/nar/gkx315
ChimeRScope, interpreted as Chimeric RNA Scope or Chi(k)-meR Scope, predicts fusion transcripts by assessing the gene fingerprint sequences. detailed information of the fusion events, fusion orientations and predicted fusion junction sequences, presented as vector-based images.
□ HadoopCNV: A Dynamic Programming Imputation Algorithm To Detect Copy Number Variants From Sequencing Data:
>> http://biorxiv.org/content/biorxiv/early/2017/04/05/124339.full.pdf
a method to combine HadoopCNV and LUMPY result, uses read depth information and alternative allele frequency information, and integrates them into a single coherent model for the most powerful detection of CNVs.
□ DrT1973:
Albacore "local" basecalling sorted on 8x32 cores, ~5Gb from 423K reads in 2h 44min.
□ SANA NetGO: A combinatorial approach to using Gene Ontology (GO) terms to score network alignments:
>> https://arxiv.org/abs/1704.01205
Similarly to how topological measures can be divided into global ones (S3, EC, WEC, etc.) and local ones (graphlet similarity, importance, etc.), so far all biological measures were strictly local. NetGO is the first global biological measure, and as in the case of topological ones, it proves to be superior to local ones in evaluating entire alignments.
□ Interrogating the topological robustness of gene regulatory circuits by randomization:
>> http://journals.plos.org/ploscompbiol/article?id=10.1371/journal.pcbi.1005456
a core gene circuit modeled by chemical rate equations and the other peripheral genes whose contribution to the network is regarded as random perturbations to the kinetic parameters of the core circuit.
□ V-ALIGN: Sequence Alignment on Directed Graphs:
>> http://biorxiv.org/content/biorxiv/early/2017/04/06/124941.full.pdf
V-ALIGN is based on a novel dynamic programming formulation that allows gapped alignment directly on the input graph. the time to fill the DP table has linear dependence on the sizes of the sequence, the graph and its feedback vertex set.
□ Arguments about (paradoxical) arguments:
>> https://blog.oup.com/2017/04/arguments-about-paradoxical-arguments/
the alternative definition of paradox, a paradox is supposed to have true premises, be truth-preserving, and have a false conclusion. But the reasoning that the argument in question has a false premise (since the argument is, in fact, paradoxical) and a true conclusion!
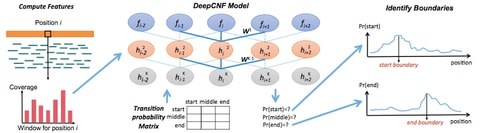
□ DeepBound: Accurate Identification of Transcript Boundaries via Deep Convolutional Neural Fields:
>> http://biorxiv.org/content/biorxiv/early/2017/04/07/125229.full.pdf
this model is trained on the reads alignment generated by Flux-Simulation RNA-seq reads followed by aligning them with real aligner (HISAT). Integrating DCNN model with CNF enables to capture the complicated underlying predicting logic buried in the millions of labeled instances. to avoid overfitting, L2-norm penalty term as the regularization factor & perform 10 fold cross validation to determine the hyper-parameter.
□ Formation of Dominant Mode by Evolution in Biological Systems:
>> http://biorxiv.org/content/biorxiv/early/2017/04/07/125278.full.pdf
a theory in which high-dimensional phenotypic changes after evolution are constrained along a one-dimensional major axis that correlates with the growth rate, which can explain broad experimental and numerical results.
□ nygenome:
5 @illumina NovaSeq systems coming soon, part of @nygenome commitment to leverage cutting-edge technologies for genomics research.
□ Index Switching Causes “Spreading-Of-Signal” Among Multiplexed Samples In Illumina HiSeq 4000 DNA Sequencing
>> http://biorxiv.org/content/biorxiv/early/2017/04/09/125724.full.pdf
illumina 3000/4000/X Ten: up to 5-10% of sequencing reads (or signals) are incorrectly assigned from a given sample to other samples in a multiplexed pool. The “spreading-of-signal” was not limited to single-cell RNA-seq libraries, but was common to all library pools (bulk RNA-seq, ATAC-seq etc.) in which samples were multiplexed and some level of free index primers were present.
□ gringene_bio:
I suspect this may be caused by chimeric reads formed during barcode / adapter ligation steps in the sample prep.
□ dritoshi:
illumina 3000/4000/X Ten が炎上中。リードの5-10%が誤ったバーコードに割り振られる。ライブラリ中のフリーなindex primer由来で、クラスタ形成前にランダムにindex が付加されてしまう。地獄か。
□ From neural network to psychophysics of time: Exploring emergent properties of RNNs using novel Hamiltonian formalism
>> http://biorxiv.org/content/biorxiv/early/2017/04/10/125849.full.pdf
the Cohen-Grossberg Liapunov function can be derived naturally from the Hamiltonian formalism. A strength of the construct comes from its usability as a predictor for behavior in psychophysical experiments involving numerosity and temporal duration judgements.
□ High Accuracy Base Calls in Nanopore Sequencing: a novel unsupervised learning to correct amplified reads.
>> http://biorxiv.org/content/biorxiv/early/2017/04/11/126680.full.pdf
DNA sequences can be interpreted as a sequence of k-mers, each k-mer can be replaced by its expected mean current to provide a mapping from DNA sequences into a high-dimensional current space.
□ DIMM-SC: A Dirichlet mixture model for clustering droplet-based single cell transcriptomic data:
>> https://arxiv.org/pdf/1704.02007.pdf
as a model-based approach, DIMM-SC is able to quantify the clustering uncertainty for each single cell, facilitating rigorous statistical inference and biological interpretations which are typically unavailable from existing clustering methods.
□ Riemannian stochastic quasi-Newton algorithm with variance reduction and its convergence analysis:
>> https://arxiv.org/pdf/1703.04890.pdf
The proposed algorithm stems from the algorithm in Euclidean space, but is now extended to Riemannian manifolds. The central difficulty of averaging, adding, and subtracting multiple gradients is handled by exploiting vector transport and retraction. R-SQN-VR generates globally convergent sequences w/a decaying step-size condition and locally linearly convergent under natural assumptions.
□ On Feature Reduction using Deep Learning for Trend Prediction in Finance:
>> https://arxiv.org/pdf/1704.03205.pdf
investigate the application of both Restricted Boltzmann Machines and Auto-Encoders in more general terms, attempting to outline how architectural and input space characteristics can affect the quality of prediction. AE is able to learn a higher dimensional structure in the input data.
□ Rust-Bio: a bioinformatics library for the Rust language:
>> https://rust-bio.github.io
□ Needletail: Fast FASTX parsing and k-mer methods in Rust: Bioinformatics toolとしては未だ稀少な、Rust言語を用いた並列高速処理.
>> https://github.com/onecodex/needletail
a simple Needletail script can count all the bases in a 2.1 gigabyte HiSeq 2500 FASTQ file in 1.1 seconds while a comparable parser with readfq takes 2.6 sec & Biopython takes over one minute (bench folder; measured w/ %timeit -r 3 -n 3, %timeit -r 3 -n 1 for Biopython).

□ Slingshot: Cell lineage and pseudotime inference for single-cell transcriptomics:
>> http://biorxiv.org/content/biorxiv/early/2017/04/19/128843.full.pdf
this novel simultaneous principal curves method for pseudotime inference extends the stability, and robustness properties of principal curves to the case of multiple branching lineages.

□ Clustering gene expression time series data using an infinite Gaussian process mixture model:
>> http://biorxiv.org/content/biorxiv/early/2017/04/26/131151.full.pdf
A Dirichlet process can determine the number of clusters in a nonparametric manner, while a Gaussian process can model the trajectory and time-dependency of gene expression in a nonparametric manner. An important advantage of DPGP is being a probabilistic method uncertainty in clustering & cluster trajectories is modeled explicitly.

□ Molecular De-Novo Design through Deep Reinforcement Learning:
>> https://arxiv.org/pdf/1704.07555.pdf
□ RIblast: An ultrafast RNA-RNA interaction prediction system based on a seed-and-extension approach:
>> https://academic.oup.com/bioinformatics/article-lookup/doi/10.1093/bioinformatics/btx287
□ Single-cell analysis of clonal dynamics in direct lineage reprogramming: combinatorial indexing for lineage tracing
>> http://biorxiv.org/content/biorxiv/early/2017/04/28/127860.full.pdf
The efficiency of these direct lineage reprogramming protocols typically ranges between 1-20%. iEP generation represents a prototypical direct lineage reprogramming methodology that reflects conversion via a progenitor-like state.

□ BasecRAWller: Streaming Nanopore Basecalling Directly from Raw Signal using RNN:
>> http://biorxiv.org/content/biorxiv/early/2017/05/01/133058.full.pdf
a basecRAWller model trained on the human data set is more robust across the two diverse data production pipelines, most likely due to the DNA translocation speed which significantly enhances challenges associated with sparse data at individual bases. unidirectional recurrent neural networks that enables the calling of DNA bases in real time directly from the rawest form of nanopore output.
□ Modeling zero-inflated count data with glmmTMB:
>> http://biorxiv.org/content/biorxiv/early/2017/05/01/132753.full.pdf
glmmTMB uses maximum likelihood estimation and the Laplace approximation to integrate over random effects. The zero-inflation model describes the probability of observing an extra / structural zero that is not generated by the conditional model. The full zero-inflated negative binomial GLMM
glmmTMB(count∼spp*mined+(1|site), ziformula=∼spp*mined, family=nbinom2, data=Salamanders).
> http://biorxiv.org/content/biorxiv/early/2017/05/01/132670.full.pdf
utilization of the idea that a given target gene is regulated by only a few TFs and proposed a novel technique based on triangle method, employed for identifying the corner in the Tikonov L-curve, to identify the optimal set of TFs for each target gene. identification of several up- stream regulators as 0-indegree nodes in the final inferred GRN.
□ Temasek, Yunfeng lead $75 million funding into China genomics firm:
>> http://www.reuters.com/article/us-wuxi-nextcode-fundraising-idUSKBN17Y0B3
WuXi NextCODE, a contract genomics organization with offices in Shanghai, Iceland and the United States, said it would use the funds to commercialize its products for China, and boost its capabilities in artificial intelligence and deep learning.
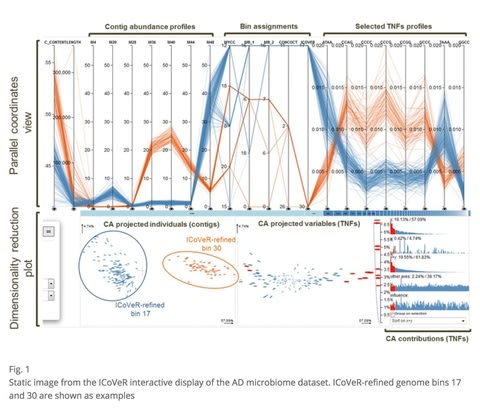
□ ICoVeR – an interactive visualization tool for verification and refinement of metagenomic bins:
>> https://bmcbioinformatics.biomedcentral.com/articles/10.1186/s12859-017-1653-5


□ LEAP: A Generalization of the Landau-Vishkin Algorithm with Custom Gap Penalties:
>> http://biorxiv.org/content/biorxiv/early/2017/05/02/133157.full.pdf
LEAP Bit-Vector is up to 7.4x faster than Levenshtein distance impl and 32x faster than affine-gap-penalty parallel Needleman Wunsch Impl. Under the parallel random-access machine model (PRAM), all the XORs can be calculated in parallel for lanes under the same energy budget e.
shift_bit_vec=bit_vec[l]≪start_pos;
rev_bit_vec=reverse_bits(shift_bit_vec);
b_LSB=rev_bit_vec∧(¬(rev_bit_vec)+1);
key=(b_LSB×dBseq)≫2n−n;
□ Deep Sequencing: Intra-terrestrial metagenomics illustrates the potential of off-grid Nanopore DNA sequencing:
>> http://biorxiv.org/content/biorxiv/early/2017/05/02/133413.full.pdf

□ Deep Phenotyping: Deep Learning for Temporal Phenotype/Genotype Classification:
>> http://biorxiv.org/content/biorxiv/early/2017/05/04/134205.full.pdf
The probability of each genotype state, SF-2, Cvi, Ler, Col, is a multivariate growth pattern phenotype of each accession, which can be decomposed into its causal genetic factors.
□ Real-time demultiplexing Nanopore barcoded sequencing data with npBarcode:
>> http://biorxiv.org/content/biorxiv/early/2017/05/04/134155.full.pdf
npBarcode using the Smith-Waterman algorithm with Gotoh improvement for the alignment.
□ LONDON CALLING 2017
- A conference hosted by Oxford Nanopore Technologies.
>> https://londoncallingconf.co.uk/lc/events/london-calling-2017
□ ewanbirney:
JS: wants to replace the HMM backbone of nanopolish with a recurrent neural network. Wants to get at the 0.1% con. error rate! #nanoporeconf
□ selectION: Rapid linking of long reads to a reference genome: reduce bioinformatic (ie. alignment) cost.
>> https://github.com/paygiesselmann/selection
□ DD: Enceladus Mission will take Nanopore-based device in ~2034. CO2, H2O, methane, ammonia. Best chance for new life! #nanoporeconf

□ Direct RNA sequencing now possible! #nanoporeconf @NanoporeConf










