
□ Circular Circuitry 🌀 / Richard Devine
>> https://vine.co/v/eTuVi3plrOU
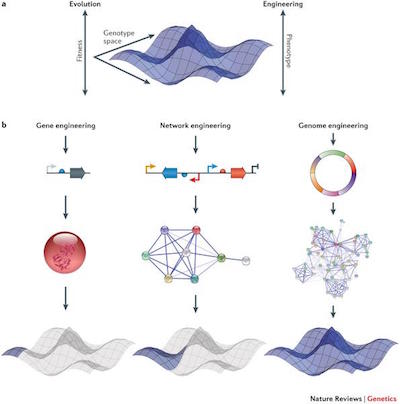
□ Genomes by design
>> http://www.nature.com/nrg/journal/v16/n9/full/nrg3956.html
Both Darwinian evolution and rational genome engineering rely on the introduction of mutations to traverse a genotype space and explore the resultant changes in cellular phenotype. The high-dimensional nature of genotype landscapes…
□ nanopore:
NASA on plans for DNA sequencing using @nanopore MinION in space
>> http://go.nasa.gov/1O6VdHR @Space_Station @ISS_Research #wateronmars

□ Automated Genomes-to-Natural Products platform for the discovery of modular natural products
>> http://www.nature.com/ncomms/2015/150928/ncomms9421/full/ncomms9421.html
a genome-guided natural products discovery tool to automatically predict, combinatorialize and identify polyketides & non ribosomal peptides from biosynthetic assembly lines using LC–MS/MS data of crude extracts in a high-throughput manner.
□ GraveleyLab:
Officially our first @nanopore RNA-Seq paper - Determining exon connectivity in complex mRNAs by nano pore sequencing
>> http://www.genomebiology.com/2015/16/1/204
□ PacBio:
Blog Post: Introducing the Sequel System - The Scalable Platform for SMRT Sequencing
>> http://ow.ly/SRsA3
The core of the Sequel System is the capacity of its redesigned SMRT Cells, which contain one million zero-mode waveguides (ZMWs) at launch, compared to 150,000 ZMWs in the PacBio RS II.
□ A multivariate Bernoulli model to predict DNaseI hypersensitivity status from haplotype data:
>> http://bioinformatics.oxfordjournals.org/content/31/21/3514.short
Comparisons of prediction under the MVB model w/ prediction under linear regression (best linear unbiased prediction) & logistic regression demonstrate that the MVB model achieves about 10% higher prediction R2 than the two competing methods in empirical data.
□ At the Edge of Chaos: How Cerebellar Granular Layer Network Dynamics Can Provide the Basis for Temporal Filters:
>> http://journals.plos.org/ploscompbiol/article?id=10.1371/journal.pcbi.1004515
simplified models of the RNN, formed by the cerebellar granular layer are capable of generating signals that can be used to construct linear exponential filters with different time constants.
The preferred alternative was ‘bottom-up’ modeling in which temporal-processing properties emerged from biologically detailed models of the granular-layer RNN rather than being imposed by a priori theoretical considerations.
it was RNNs with small, negative values of Lyapunov exponents, representing this intermediate ‘edge-of-chaos’ region that generated long-lasting and complex responses to transient inputs.
□ SBGenomics:
Thrilled to help improve reproducibility in bioinformatics by way of common workflow language #CWL
>> https://www.genomeweb.com/informatics/seven-bridges-funds-uc-davis-support-development-standardized-workflow-language …
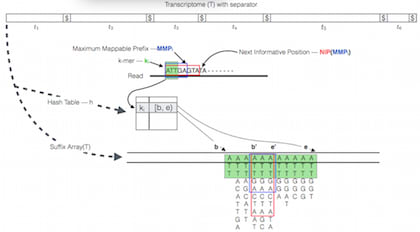
□ RapMap: A Rapid, Sensitive and Accurate Tool for Mapping RNA-seq Reads to Transcriptomes:
>> http://biorxiv.org/content/biorxiv/early/2015/10/22/029652.full.pdf
it's more like an "all-best" mapper, since it returns all hits in the top "stratum" of lightweight/pseudo/quasi alignments. RapMap also exposes an independent, multi-threaded re-implementation of the concept of pseudo-alignment as originally introduced in Kallisto.
Quasi-mapping determines the mapping locations for a query read r through repeated application of computing the maximum mappable prefix (MMP) of the query beginning with this k-mer, determining the next hashable k-mer that starts past the current query position, and then determining the next informative position (NIP) by performing a longest common prefix (LCP) query on two specifically chosen suffixes in the suffix array.

□ PCGSE: Principal component gene set enrichment
>> http://www.biodatamining.org/content/pdf/s13040-015-0059-z.pdf
Gene set testing is an effective approach for interpreting the PCs of high-dimensional genomic data. As shown using both simulated and real datasets, the PCGSE method can generate biologically meaningful and computationally efficient results via a two-stage, competitive parametric test that correctly accounts for inter-gene correlation.
PCGSE was used to compute the statistical association between 20 disjoint gene sets, each of size 10, against the PCs of 1,000 simulated GE, each comprised by 75 independent observations of a 200-dimensional random vector simulated to a multivariate normal distribution ∼ MVN(μ, Σ)
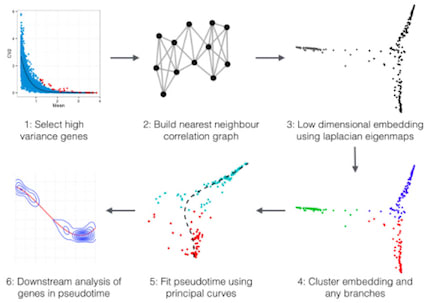
□ Laplacian eigenmaps and principal curves for high resolution pseudotemporal ordering of single-cell RNA-seq profiles:
>> http://biorxiv.org/content/biorxiv/early/2015/09/18/027219.full.pdf
Embeddr employs non-linear dimensionality reduction of the gene-space - a manifold learning technique. In scRNA-seq data cells are represented by GE vectors, 20,000+ dimensions depending on whether individual transcripts are considered. this method combines many of the strengths of current methods such as the graph based Wanderlust and ICA-based Monocle.
□ GenomeNathan:
Graph genomes cometh: October 13 @nygenome hosts @GA4GH's Data Working Group, to unveil & start using graph refs.
>> http://ga4gh.org/#/oct2015meeting
□ Generalised empirical Bayesian methods for discovery of differential data in high-throughput biology:
>> http://biorxiv.org/content/early/2015/09/25/011890
a highly flexible solution (baySeq v2) to the general problem of identifying differential behavior, in the ‘large P,small n’ sets of data that are becoming ubiquitous in biological experimentation (and elsewhere).
In all cases, baySeq v2 with a zero-inflated negative binomial model outperforms ShrinkBayes, especially for low sequencing depths.
if a RNA-seq data under an assumption of negative binomially distributed data & a ChIP-Seq data under a Dirichlet-multinomial distribution, it is straightforward to calculate joint likelihoods of specific patterns of differential expression of RNA-Seq and ChIP-Seq.
□ Determination of nonlinear genetic architecture using compressed sensing:
>> http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4570224/
the proposed method can recover a significant fraction of the predictive power (equivalently, variance) associated with nonlinear effects.
The L1 penalization (e.g., LASSO) involves minimization of an objective function O over candidate vectors xˆ:
O=∣∣y-Axˆ∣∣L2+λ∣∣xˆ∣∣L1,
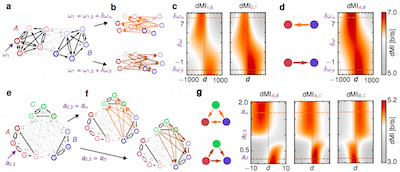
□ Dynamic information routing in complex networks
>> http://biorxiv.org/cgi/content/short/029405v1
a theoretical basis for the emergence of information routing capabilities in complex networks when signals are communicated on top of collective reference states.
on long time scales, evolutionary pressure may select a particular information routing pattern by biasing a particular collective state in gene regulatory and cell signaling networks.
on intermediate time scales, local changes in neuronal responses due to adaptation or varying synaptic coupling strength during learning processes can impact information routing paths in entire neuronal circuits.
on fast time scales, defined control inputs to biological networks or engineered communication systems that switch the underlying collective state can dynamically modulate information routing patterns without any physical change to the network.

□ Fitting a neural network in R; neuralnet package:
>> http://www.r-bloggers.com/fitting-a-neural-network-in-r-neuralnet-package/
implement a fast cross validation using a for loop for the neural network and the cv.glm() function in the boot package for the linear model.
pr.nn
□ HGVM: Human Genome Variation Map to create a draft reference structure that represents all common genetic variation:
>> https://github.com/ga4gh/schemas/wiki/Human-Genome-Variation-Map-(HGVM)-Pilot-Project
□ The Problem with Phi: A Critique of Integrated Information Theory:
>> http://journals.plos.org/ploscompbiol/article?id=10.1371/journal.pcbi.1004286
The intuitively nonconscious systems can generate arbitrarily high values of Φ suggests that IIT is a theory of noncognitive-consciousness. Researchers in artificial general intelligence and consciousness can be reassured that IIT does not banish the ghosts from their machines.
“the amount of information generated by a complex of elements, above and beyond the information generated by its parts”
□ CLAMMS: a scalable algorithm for calling common and rare copy number variants from exome sequencing data:
>> http://bioinformatics.oxfordjournals.org/content/early/2015/09/15/bioinformatics.btv547.full.pdf
CLAMMS collects 7 QC metrics and performs a fast k-nearest neighbors search algorithm (k=100) implemented using a k-d tree data structure.
□ Plotly: Graphing and dashboards for bioinformatics and the modern life sciences.
>> https://plot.ly/products/industries/pharma/#readon
□ Introducing scikit-allel for analysis of large-scale genome variation data:
>> http://alimanfoo.github.io/2015/09/15/introducing-scikit-allel.html
□ MLDB is the Machine Learning Database:
>> http://mldb.ai
□ Probabilistic Boolean Modeling and Analysis Framework for mRNA translation:
>> http://ieeexplore.ieee.org/xpl/articleDetails.jsp?arnumber=7265002
which possesses the advantage of tools for numerically exact computation of steady state probability distribution, w/o requiring simulation. extend this model to incorporate both random sequential and parallel update rules, and demonstrate its effectiveness in various settings, incl. its flexibility in accommodating additional static and dynamic biological complexities and its role in parameter sensitivity analysis.
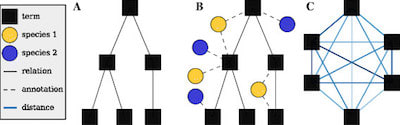
□ htsint: a Python library for seq pipelines that combines data through gene set generation:
>> http://www.biomedcentral.com/1471-2105/16/307
the Gene Ontology graph is trimmed and the edges are weighted by estimating all term-term distances―a computationally intensive step. The distance is where differences in the Information Content of semantic entities are employed as a measure of the semantic distance.
□ deeplearning4j:
An interview with Brendan Frey of Deep Genomics
>> http://www.news-medical.net/news/20150921/Using-deep-learning-to-analyze-genetic-mutations-an-interview-with-Brendan-Frey.aspx … #deeplearning #genomics
□ A Critical Review of Recurrent Neural Networks for Sequence Learning:
>> http://arxiv.org/abs/1506.00019
□ Do we Need Hundreds of Classifiers to Solve Real World Classification Problems?
>> http://jmlr.csail.mit.edu/papers/volume15/delgado14a/delgado14a.pdf
The random forest is clearly the best family of classifiers, followed by SVM, neural networks and boosting ensembles.
□ Diving deeper to predict noncoding sequence function:
>> http://www.nature.com/nmeth/journal/v12/n10/full/nmeth.3604.html
The deep learning–based method DeepSEA predicts the molecular function of noncoding DNA polymorphisms.
□ ExSTraCS 2.0: description and evaluation of a scalable learning classifier system:
>> http://link.springer.com/article/10.1007%2Fs12065-015-0128-8
ExSTraCS 2.0 addresses scalability with a rule specificity limit, new approaches to expert knowledge guided covering and mutation mechanisms and the implementation and utilization of the TuRF algorithm for improving the quality of expert knowledge discovery in larger datasets.

□ cl-dash: rapid configuration & deployment of Hadoop clusters for bioinformatics in the cloud
>> http://bioinformatics.oxfordjournals.org/content/early/2015/09/30/bioinformatics.btv553.abstract
□ Stochastic Analysis Of An Incoherent Feedforward Genetic Motif:
>> http://biorxiv.org/content/early/2015/09/30/028019

Schemetic figure of a feedforward circuit regulated by a biological switch.
while feedforward systems can buffer a protein from noise in its upstream regulators, noise can propagate downstream due to changes in the time-scale of fluctuations.
□ Fractality and Entropic Scaling in the Chromosomal Distribution of Conserved Noncoding Elements in the Human Genome:
>> http://biorxiv.org/content/early/2015/09/28/027763
the fractal pattern has been revealed because the contact probability as a function of genomic distance across the genome shows a power law scaling at an important range of lengths.
□ tuuliel:
My thoughts on bridging statistical genetics and molecular biology in a Genome Research perspective paper:
>> http://genome.cshlp.org/cgi/content/long/25/10/1427
The most important gap in the current literature concerns trans-eQTLs associations to distal genes in the human genome. predictive imputation of gene expression levels in individuals, based on genotype data, is becoming possible.
□ Deep learning the relationship between chromatin architecture, chromatin state, and transcription factor binding: #ASHG15
>> https://ep70.eventpilotadmin.com/web/page.php?page=IntHtml&project=ASHG15&id=150123208 …
Using a multi-task, multi-modal formulation integrate ATAC-seq data, DNA-shape and DNA-sequence to simultaneously predict multiple histone modifications, chromatin state and TF binding with high accuracy (80-90%).
□ A deep learning framework for modeling structural features of RNA-binding protein targets:
>> http://nar.oxfordjournals.org/content/early/2015/10/13/nar.gkv1025.short
the increased number of hits in the IRES regions produced by DBN+3D was not attributed to the false-positive issue, in other words, deep learning method did not suffer from the false positive problem.
□ Quantum Coherent-like State Observed in a Biological Protein for the First Time:
>> https://www.aip.org/publishing/journal-highlights/quantum-coherent-state-observed-biological-protein-first-time
The presence of collective vibrational excitation in biomolecules gives extensive consequences on the self-organization within cells and on the non-equilibrium thermodynamics of reactions involving protein molecules. different intensities of terahertz radiation may alter the Boltzmann factor between vibrational states, making the protein reaction rates dependent on the terahertz radiation drive rather than the temperature in thermal equilibrium.
□ SIGNOR: a database of causal relationships between biological entities:
>> http://nar.oxfordjournals.org/content/early/2015/10/13/nar.gkv1048.full
SIGNOR stores more than 12,000 causal relationships between cellular components, originating from a de novo curation effort or from external DBs (PhosphositePlus, PhosphoELM, IMEx databases and SignaLink) The information captured in SIGNOR can be represented as a signed directed graph illustrating activation/inactivation b/n signaling entities.
□ GenoSkyline: Integrative tissue-specific functional annotations: human genome on many complex traits & GWAS improve
>> http://biorxiv.org/content/early/2015/10/06/028464
GenoSkyline is an unsupervised learning framework to predict tissue-specific functional regions through integrating epigenetic annotations.
□ ym_duality:
>> https://kaken.nii.ac.jp/d/p/15H06313.en.html
「数学基礎論と量子基礎論の圏論的統合と機械学習における圏論的双対性へのその応用」(前半はトポス的空間概念と量子論的空間概念のhyperdoctrinalな融合;再生核ヒルベルト空間とカーネル函数/ガウス過程の間の双対性が後半の応用)










