
□ Aristotle: stratified causal discovery for omics data
>> https://bmcbioinformatics.biomedcentral.com/articles/10.1186/s12859-021-04521-w
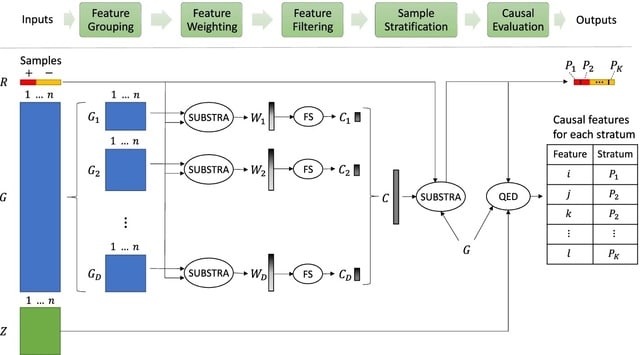
Aristotle is a multi-phase algorithm that tackles the above challenges by using a novel divide-and-conquer scheme that utilizes biclustering for finding the promising strata and candidate causes and QED to identify the stratum-specific causes.
Aristotle detects the hidden strata using SUBSTRA. SUBSTRA learns feature weights, and uses these weights when computing the strata. Aristotle needs to evaluate the causality of the association between each of the candidate features and each of the positive strata.

□ Improving the time and space complexity of the WFA algorithm and generalizing its scoring
>>
The time complexity of Wavefront Algorithm (WFA) is O(sN), taking N = min{M,N} without loss of generality. It may need to perform O(N) character comparisons over the course of the algorithm. The algorithm requires O(s2) additional space over and above the O(M + N) space.
The suffix tree-based algorithm required significantly more time than the direct comparison algorithm. This contrasts with the suffix tree algorithm’s favorable asymptotic time complexity, these sequences are insufficiently divergent for the asymptotic behavior to set in.
Refinements of the WFA alignment algorithm with better complexity. These variants WFA that improve its asymptotic memory use from O(s^2) to O(s^3/2) and its asymptotic run time from O(sN) to O(s^2 +N).

□ The minimizer Jaccard estimator is biased and inconsistent
>> https://www.biorxiv.org/content/10.1101/2022.01.14.476226v1.full.pdf
The minimizer Jaccard estimator is biased and inconsistent, which means that the expected difference (i.e., the bias) between the estimator and the true value is not zero, even in the limit as the lengths of the sequences grow.
An analytical formula for the bias as a function of how the shared k-mers are laid out along the sequences. Both theoretically and empirically that there are families of sequences where the bias can be substantial e.g. the true Jaccard can be more than double the estimate.
□ Power analysis for spatial omics
>> https://www.biorxiv.org/content/10.1101/2022.01.26.477748v1.full.pdf
An in silico tissue framework to enable spatial power analysis and assist with experimental design. ISTs can be directly used for method development and benchmarking of existing or novel spatial analysis methods.
In silico tissues were generated by first constructing a tissue scaffold - a blank tissue with no cell information assigned - then assigning cell type labels to the scaffold.
a beta-binomial model to predict how many single cells need to be measured to observe a cell type of interest at a certain probability and a gamma-Poisson model to predict how many FOVs are required to observe a cell type of interest at a certain probability.

□ NGSEP 4: Efficient and Accurate Identification of Orthogroups and Whole Genome Alignment
>> https://www.biorxiv.org/content/10.1101/2022.01.27.478091v1.full.pdf
NGSEP implements functionalities for identification of clusters of homologus genes, synteny analysis and whole genome alignment, and visualization. Clustering is performed from the graph running Markov Clustering on the connected components.
If genome assemblies are provided as input, synteny relationships are identified for each pair of genomes implementing an adapted version of the HalSynteny algorithm.
A synteny block is identified making a single traversal, and calculating for each vertex the total length of the longest path that finishes. The vertex with the longest global path length is chosen as the last vertex of the synteny path and predecessors reconstruct the path.

□ SNP calling for the Illumina Infinium Omni5-4 SNP BeadChip kit using the butterfly method
>> https://www.biorxiv.org/content/10.1101/2022.01.17.476594v1.full.pdf
the “butterfly method” for SNP calling with the Illumina Infinium Omni5-4 BeadChip kit without the use of Illumina GenomeStudio software. The method is a within-sample method and does not use other samples nor population frequencies to call SNPs.
By lowering the a posteriori probability threshold for no-calls, we can get a higher call rate fraction than the GenomeStudio and by using a higher a posteriori probability threshold, we can achieve a higher concordance with the WGS data.

□ SLAG: A Program for Seeded Local Assembly of Genes in Complex Genomes
>> https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1111/1755-0998.13580
SLAG (Seeded Local Assembly of Genes) fulfills this need by performing iterative local assembly based on cycles of matching-read retrieval with blast and assembly with CAP3, phrap, SPAdes, canu, or Unicycler.
Read fragmentation allows SLAG to use phrap or CAP3 to assemble long reads at lower coverage (e.g., 5x) than is possible with canu or Unicycler.
a SLAG assembly can cover a whole chromosome, but in complex genomes the growth of target-matching contigs is limited as additional reads are consumed by consensus contigs consisting of repetitive elements.

□ scCorr: A novel graph-based k-partitioning approach improves the detection of gene-gene correlations by single-cell RNA sequencing
>> https://bmcgenomics.biomedcentral.com/articles/10.1186/s12864-021-08235-4
scCorr uses a graph-based algorithm to recover the missing gene-gene correlation in scRNA-seq data that enables the reliable acquisition of cluster-based gene-gene correlations in three independent scRNA-seq datasets.
The scCorr algorithm generates a graph or topological structure, and partitioning the graph into k multiple min-clusters employing the Louvain algorithm. And averaging the expression values, including zero values.

□ DENTIST-using long reads for closing assembly gaps at high accuracy
>> https://academic.oup.com/gigascience/article/doi/10.1093/gigascience/giab100/6514926
DENTIST determines repetitive assembly regions to identify reliable and unambiguous alignments of long reads to the correct loci, integrates a consensus sequence computation to obtain a high base accuracy for the inserted sequence, and validates the accuracy of closed gaps.
DENTIST improves the contiguity and completeness of fragmented assemblies with long reads. DENTIST uses the first 3 repeat annotations as a soft mask/aligns all input long reads to the assembly using damapper, which outputs chains of local alignments arising from read artefacts.

□ ECCsplorer: a pipeline to detect extrachromosomal circular DNA (eccDNA) from next-generation sequencing data
>> https://bmcbioinformatics.biomedcentral.com/articles/10.1186/s12859-021-04545-2
Following Illumina-sequencing of amplified circular DNA (circSeq), the ECCsplorer enables an easy and automated discovery of eccDNA candidates.
The ECCsplorer pipeline provides a framework for the automated detection of eccDNA candidates using well established tools including data transfer between tools, data summarization and assessment.

□ Using dual-network-analyser for communities detecting in dual networks
>> https://bmcbioinformatics.biomedcentral.com/articles/10.1186/s12859-022-04564-7
Dual-Network-Analyser is based on the identification of communities that induce optimal modular subgraphs in the conceptual network and connected subgraphs in the physical one. It includes the Louvain algorithm applied to the considered case.
The Dual-Network-Analyser algorithm receives as input two input networks. Networks are initially merged into a single Weighted Alignment Graph. The Louvain algorithm is used for finding them modular communities, while in the case of DCS, then the Charikar algorithm is used.

□ Acidbio: Assessing and assuring interoperability of a genomics file format
>> https://www.biorxiv.org/content/10.1101/2022.01.07.475366v1.full.pdf
Bioinformatics software tools operate largely through the use of specialized genomics file formats. Often these formats lack formal specification, and only rarely do the creators of these tools robustly test them for correct handling of input and output.
Acidbio provides a test system for software that parses the BED format as input. Acidbio unifies correct behavior when tools encounter various edge cases—potentially unexpected inputs that exemplify the limits of the format.

□ oCEM: Automatic detection and analysis of overlapping co-expressed gene modules
>> https://bmcgenomics.biomedcentral.com/articles/10.1186/s12864-021-08072-5
Overlapping CoExpressed gene Module (oCEM) did the extraction of non-Gaussian signatures by ICA - the fastICA algorithm was configured using parallel extraction method and the default measure of non-Gaussianity logcosh approximation of negentropy with α = 1.
optimizeCOM specifies the optimal number of principal components in advance required by the decomposition methods. the processed data were inputted into the function overlapCEM, rendering co-expressed gene modules (i.e., Signatures with their own kurtosis ≥ 3) and Patterns.

□ Transitivity scores to account for triadic edge weight similarity in undirected weighted graphs
>> https://www.biorxiv.org/content/10.1101/2022.01.11.475816v1.full.pdf
The graph transitivity is usually computed for dichotomized networks, therefore focusing on whether triangular relationships are closed or open. But when the connections vary in strength, focusing on whether the closing ties exist or not can be reductive.
Scoring the weighted transitivity according to the similarity between the weights of the three possible links in each triad. It correctly diagnosed excesses of balanced or imbalanced triangles, e.g. strong triplets closed by weak links.
□ Debiasing FracMinHash and deriving confidence intervals for mutation rates across a wide range of evolutionary distances
>> https://www.biorxiv.org/content/10.1101/2022.01.11.475870v1.full.pdf
While there is ample computational evidence for the superiority of FracMinHash when compared to the classic MinHash, particularly when comparing sets of different sizes, no theoretical characterization about the accuracy of the FracMinHash approach has yet been given.
FracMinHash can estimate the true containment index better when the sizes of two sets are dissimilar. One particularly attractive feature of FracMinHash is its analytical tractability.

□ An accurate method for identifying recent recombinants from unaligned sequences
>> https://academic.oup.com/bioinformatics/advance-article/doi/10.1093/bioinformatics/btac012/6506517
An algorithm to detect recent recombinant sequences from a dataset without a full multiple alignment. This algorithm can handle thousands of gene-length sequences without the need for a reference panel.
This framework develops on the basis of the paritial alignment results from jumping hidden markov model (JHMM), after that, by dividing them into multiple equal-length triples, on which they use a new distance-based procedure to identify recombinant from each triple.

□ Slinker: Visualising novel splicing events in RNA-Seq data
>> https://f1000research.com/articles/10-1255
Slinker, a bioinformatics pipeline written in Python and Bpipe that uses a data-driven approach to assemble sample-specific superTranscripts.
Slinker uses Stringtie2 to assemble transcripts with any sequence across any gene. This assembly is merged with reference transcripts, converted to a superTranscript, of which rich visualisations are made through Plotly with associated annotation and coverage information.
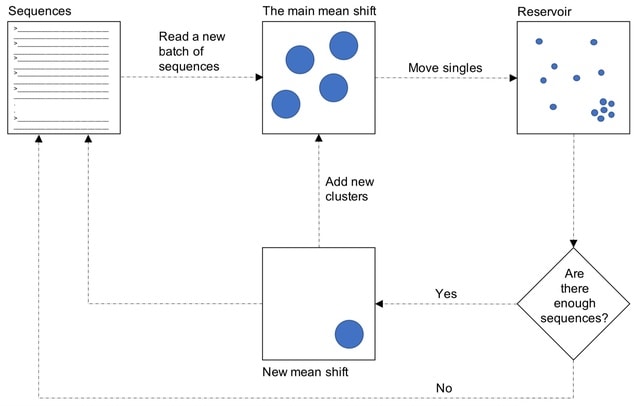
□ MeShClust v3.0: High-quality clustering of DNA sequences using the mean shift algorithm and alignment-free identity scores
>> https://www.biorxiv.org/content/10.1101/2022.01.15.476464v1.full.pdf
MeShClust v3.0 is based on the mean shift algorithm, which is an instance of unsupervised learning. The scaled-up MeShClust v3.0 is also an instance of out-of-core learning, in which the learning algorithm is trained on separate batches of the training data consecutively.
MeShClust v3.0 utilizes the k-means clus- tering algorithm with a k value of 2. To determine the maximum center-member identity score, MeShClust v3.0 reads 10,000 sequences. It calculates all-versus-all identity scores on these sequences using Identity.

□ ONTdeCIPHER: An amplicon-based nanopore sequencing pipeline for tracking pathogen variants
>> https://academic.oup.com/bioinformatics/advance-article-abstract/doi/10.1093/bioinformatics/btac043/6515611
ONTdeCIPHER integrates 13 bioinformatics tools, including Seqkit, ARTIC bioinformatics tool, PycoQC, MultiQC, Minimap2, Medaka, Nanopolish, Pangolin (with the model database pangoLEARN), Deeptools (PlotCoverage, BamCoverage), Sniffles, MAFFT, RaxML and snpEff.
While building on the main features of the ARTIC pipeline, the ONTdeCIPHER pipeline incorporates additional useful features such as variant calling, variant annotation, lineage inference, multiple alignments and phylogenetic tree construction.

□ conST: an interpretable multi-modal contrastive learning framework for spatial transcriptomics
>> https://www.biorxiv.org/content/10.1101/2022.01.14.476408v1.full.pdf
conST can learn low-dimensional embeddings by effectively in- tegrating multi-modal SRT data, i.e. gene expression, spatial information, and morphology to learn low-dimensional embeddings.
The GNNExplainer explains which neighboring spots contribute to the prediction that conST makes, which is also biologically consistent with the interaction of the L-R pair identified in CCI.

□ NIMAA: an R/CRAN package to accomplish NomInal data Mining AnAlysis
>> https://www.biorxiv.org/content/10.1101/2022.01.13.475835v1.full.pdf
NIMAA can select a larger sub-matrix with no missing values in a matrix containing missing data, and then use the matrix to generate a bipartite graph and cluster on two projections.
NIMAA provides functions for constructing weighted and unweighted bipartite graphs, analysing the similarity of labels in nominal variables, clustering labels or categories to super-labels, validating clustering results, predicting bipartite edges by missing weight imputation.

□ Varia: a tool for prediction, analysis and visualisation of variable genes
>> https://bmcbioinformatics.biomedcentral.com/articles/10.1186/s12859-022-04573-6
Varia predicts near full-length gene sequences and domain compositions of query genes from database genes sharing short sequence tags. Varia generates output through two complementary pipelines.
Varia_VIP returns all putative gene sequences and domain compositions of the query gene from any partial sequence provided, thereby enabling experimental validation of specific genes of interest and detailed assessment of their putative domain structure.
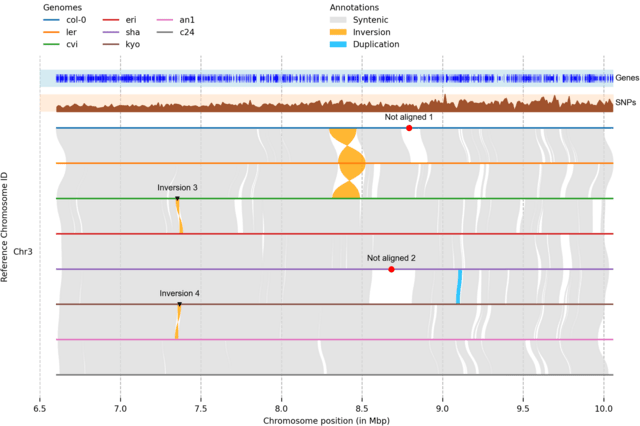
□ plotsr: Visualising structural similarities and rearrangements between multiple genomes
>> https://www.biorxiv.org/content/10.1101/2022.01.24.477489v1.full.pdf
Plotsr generates high-quality visualisation of synteny and structural rearrangements between multiple genomes. For this it uses the genomic structural annotations between multiple chromosome-level assemblies.
plotsr can be used to compare multiple haploid genomes as well as different haplotypes of individual polyploid genomes. In addition, plotsr can mark specific loci as well as plot histogram tracks to show distributions of genomic features along the chromosomes.

□ BioInfograph: An Online Tool to Design and Display Multi-Panel Scientific Figure Interactively
>> https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fgene.2021.784531/full
bioInfograph, a web-based tool that allows users to interactively arrange high-resolution images in diversified formats, mainly Scalable Vector Graphics (SVG), to produce one multi-panel publication-quality composite figure.
bioInfograph solves stylesheet conflicts of coexisting SVG plots, integrates a rich-text editor, and allows creative design by providing advanced functionalities like image transparency, controlled vertical stacking of plots, versatile image formats, and layout templates.

□ Nanopore adaptive sampling: a tool for enrichment of low abundance species in metagenomic samples
>> https://genomebiology.biomedcentral.com/articles/10.1186/s13059-021-02582-x
A mathematical model which can predict the enrichment levels possible in a metagenomic community given a known relative abundance and read length distribution.
Using a synthetic mock community, the predictions of the model correlate well with observed behaviour and quantify the negative effect on flow cell yields caused by employing adaptive sampling.
The use of adaptive sampling provides us with the benefits of library-based enrichment, without complex protocols or the bias that these may introduce. The repeated ejection of molecules from the pores had less effect on pore stability than has been previously reported.

□ FMSClusterFinder: A new tool for detection and identification of clusters of sequential motifs with varying characteristics inside genomic sequences
>> https://www.biorxiv.org/content/10.1101/2022.01.23.474238v1.full.pdf
FMSClusterFinder, a new algorithm for identification and detection of clusters of sequential blocks inside the DNA and RNA subject sequences. Gene expression and genomic groups' performance is under the control of functional elements cooperating with each other as clusters.
The functional blocks are often comparably short, degenerate and are located within varying distances from each other. Since functional motifs mostly act in relation to each other as clusters, finding such clusters of blocks is to identify functional groups and their structure.
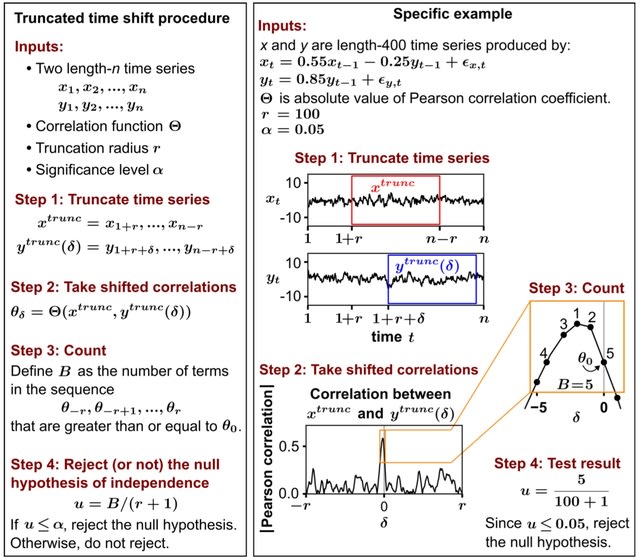
□ An exactly valid and distribution-free statistical significance test for correlations between time series
>> https://www.biorxiv.org/content/10.1101/2022.01.25.477698v1.full.pdf
The truncated time-shift (TTS), a statistical hypothesis test of dependence between two time series which can be used with any correlation function and which is valid as long as one of the time series is stationary.
This is a minimally restrictive requirement among exactly valid nonparametric tests of dependence between time series. This test was able to verify the previously observed dependences between obliquity and deglaciation timing.

□ MM4LMM: Efficient ReML inference in variance component mixed models using a Min-Max algorithm
>> https://journals.plos.org/ploscompbiol/article?id=10.1371/journal.pcbi.1009659
a Min-Max (MM) algorithm for the ReML inference in Gaussian Variance Component (VC) mixed model. The MM algorithm can be combined to the classical tricks used to accelerate the inference process (e.g. simultaneous orthogonalization or squared iterative acceleration methods).
A limitation for such further developments is the fact that MM methods require the derivation of a specific surrogate function for each class of mixed model to be considered, making the extension of the inference procedure to e.g. auto-regressive or factor analytic models not straightforward.

□ Detecting gene–gene interactions from GWAS using diffusion kernel principal components
>> https://bmcbioinformatics.biomedcentral.com/articles/10.1186/s12859-022-04580-7
This approach employs kernel PCA on a “sandwich” kernel matrix which contains a diffusion kernel as “filling”. The dimensions of the “sandwich” kernel are determined by the available number of individuals in the study.
Interaction information between SNPs allocated to the same gene is used to compute diffusion kernels and graphical within-gene network structures. Data reduction via kernel PCA gives gene summaries that are submitted to an epistasis detection model of choice.

□ Tricycle: Universal prediction of cell-cycle position using transfer learning
>> https://genomebiology.biomedcentral.com/articles/10.1186/s13059-021-02581-y
Tricycle predicts a cell-specific position in the cell cycle based on the data projection. Tricycle generalizes across datasets and is highly scalable and applicable to atlas-level single-cell RNA-seq data.
Tricycle is a locked-down prediction procedure. There are no tuning parameters, neither explicitly set nor implicitly set through the use of cross-validation or alternatives.

□ MUON: multimodal omics analysis framework
>> https://genomebiology.biomedcentral.com/articles/10.1186/s13059-021-02577-8
MUON comes with interfaces to multi-omics analysis methods that jointly process multiple modalities, including multi-omics factor analysis (MOFA) to obtain lower-dimensional representations, and weighted nearest neighbours (WNN) to calculate multimodal neighbours.
At the core of MUON is MuData (multimodal data)—an open data structure for multimodal datasets. MuData handles multimodal datasets as containers of unimodal data. MuData provides a coherent structure for storing associated metadata and other side information.

□ ClustAssess: tools for assessing the robustness of single-cell clustering
>> https://www.biorxiv.org/content/10.1101/2022.01.31.478592v1.full.pdf
ClustAssess provides fine-grained information enabling (a) the detection of optimal number of clusters, (b) identification of regions of similarity (and divergence) across methods, (c) a data driven assessment of optimal parameter ranges.
ClustAssess comprises functions for evaluating clustering stability with regard to the number of clusters using proportion of ambiguous clusterings, functions for quantifying per-observation agreement between two or more clusterings using element-centric clustering comparison.

□ SeqWho: Reliable, Rapid Determination of Sequence File Identity using k-mer Frequencies in Random Forest Classifiers
>> https://academic.oup.com/bioinformatics/advance-article/doi/10.1093/bioinformatics/btac050/6520802
SeqWho, a program designed to assess heuristically the quality of sequencing files and reliably classify the organism and protocol type by using Random Forest classifiers trained on biases native in k-mer frequencies and repeat sequence identities.
While there are some errors in the heuristic assessment of quality, SeqWho remains able to very accurately characterize the file’s quality substantially faster than FASTQC.
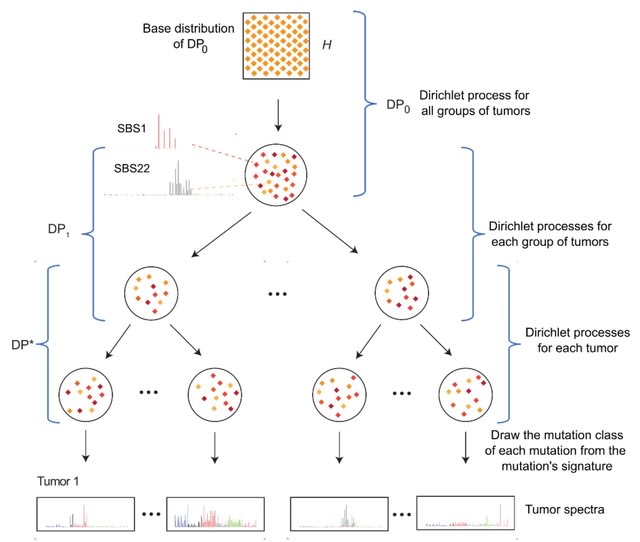
□ mSigHdp: hierarchical Dirichlet process mixture modeling for mutational signature discovery
>> https://www.biorxiv.org/content/10.1101/2022.01.31.478587v1.full.pdf
The hierarchical Dirichlet process (HDP) mixture model’s estimate of the number of signatures is influenced by the prior gamma distributions of the Dirichlet-process concentration parameters.
mSigHdp and SigProfilerExtractor had different strengths, with mSigHdp less susceptible to false negatives and SigProfilerExtractor less susceptible to false positives.




















※コメント投稿者のブログIDはブログ作成者のみに通知されます