
□ 『価値』は、交換のダイナミクスによって決定され、そう見えればいい影踏みのようなものでもあるが、『意味』は、その符号的実体の力学的な局在構造を投影している。これは『意味論構造』の反転であり、ある種の演算子を通して可換であると考えている。
□ 決定論と自由意思が契約関係にあるならば、architectureの意味論的な遷移のプロセスにおいて可塑性を担保する擬証が起こり得る。
□ DeepArchitect: Automatically Designing Deep Architectures: LISP-like language to search architectures & hyperparams.
>> https://arxiv.org/pdf/1704.08792.pdf
The model evaluation algorithm determines how to compute a score for a model in the search space.
(Concat
(Conv2D [32, 64] [3, 5] [1])
(MaybeSwap BatchNormalization ReLU)
(Optional (Dropout [0.5, 0.9]))
(Affine [10]))
□ Slow diffusive dynamics in a chaotic balanced neural network:
>> http://journals.plos.org/ploscompbiol/article?id=10.1371/journal.pcbi.1005505
For large enough (but realistic) neural population sizes, and with suitable tuning of the network connections, sustain continuous parameter values in memory over time scales larger by several orders of magnitude than the single neuron time scale.
□ CATALYST: Cytometry dATa anALYSis: normalization bead standards, single-cell deconvolution & bead-based compensation
>> https://bioconductor.org/packages/devel/bioc/manuals/CATALYST/man/CATALYST.pdf
Mass cytometry provides the highly dimensional analytic platform necessary to capture many of the known relevant phenotypical traits. While the true time dimension of cell differentiation cannot be elucidated by this approach, sequentially ordering cells according to their developmental trajectory provides a way to infer the sequence of cellular events across development.
# apply deconvolution parameters
re <- estCutoffs(re)
re <- applyCutoffs(x = re)
plotEvents(x = re, which = "D1", n_events = 500)
□ Horizontal gene transfer is not a hallmark of the human genome
>> https://genomebiology.biomedcentral.com/articles/10.1186/s13059-017-1214-2
the vast majority of human genes presence to normal process of inheritance by vertical descent. no genes have been horizontally transferred.
□ Maximum entropy framework for inference of cell population heterogeneity in signaling networks:
>> http://biorxiv.org/content/biorxiv/early/2017/05/12/137513.full.pdf
the maximum entropy framework naturally avoids over-constraining the parameter distribution; Lagrange multipliers corresponding to redundant constraints automatically evaluate to zero.
□ Variation after response in quantum Monte Carlo:
>> http://aip.scitation.org/doi/10.1063/1.4961686
the Schrödinger equation is diagonalized in a subspace of Hilbert space spanned by the first derivatives of the ground state. The JAGP ansatz in Hilbert space has been investigated previously for ground states and for excited states via both the minimization of Ω and the use of a VMC-based EOM formalism.
□ Applying Principal Component Analysis to a data-set of short electronic music loops:
>> https://www.math.uci.edu/~isik/posts/Eigentechno.html
Since SVD is trying to minimize the distance between its data-points and each of their lower-dimensional reconstructions, it makes sense that it would prioritize low frequencies.
1万曲の電子音楽のデータからPCAによる固有ベクトルの解析。
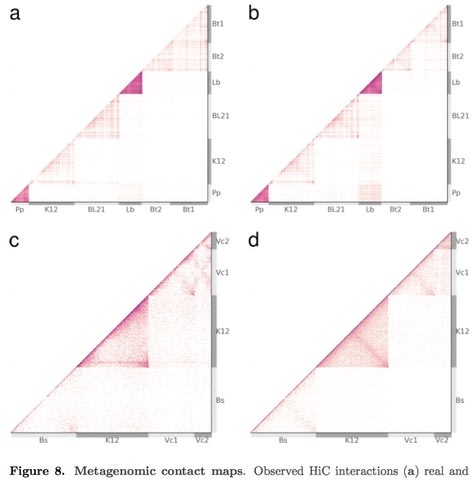
□ Sim3C: simulation of HiC and Meta3C proximity ligation sequencing technologies:
>> http://biorxiv.org/content/biorxiv/early/2017/05/15/134452.full.pdf
Sim3C models machine-based sequencing error, formation of spurious ligation products & the contamination of PL libraries w/ WGS read-pairs. Beyond primary intra-chromosomal interactions which produce the main diagonal, Sim3C can reproduce an inter-arm mediated anti-diagonal at user controlled intensity.


□ Clusternomics: Integrative Context-Dependent Clustering for Heterogeneous Datasets:
>> http://biorxiv.org/content/biorxiv/early/2017/05/17/139071.full.pdf
the probabilistic model behind the algorithm, which is closely related to the hierarchical Dirichlet process. This circumvents the problem of large dimensionality of the space of potential cluster combinations across contexts.
□ Molecular Dynamics and Machine Learning Create ‘Hyper-predictive’ Models for Drug Discovery:
>> https://news.ncsu.edu/2017/05/fourches-hyper-predictive-model/
the docking of 87 ERK2 ligands with known binding affinities was accomplished using Schrodinger’s Glide software. MD descriptors could enable the hyper-predictive MD-QSAR models for computer-aided lead optimization and analogue prioritization.
□ Mobius Assembly: a versatile framework for Golden Gate assembly:
>> http://biorxiv.org/content/biorxiv/early/2017/05/19/140095.full.pdf
Golden Braid 2.0 framework uses a simple pairwise approach where multipartite expansion is achieved by switching between 2 levels, α and Ω. MoClo framework uses a complex, yet high capacity vector toolkit to achieve parallel assembly. Mobius Assembly is based on a 2-level approach & embraces the standard overhangs defined by MoClo & Golden Braid to confer exchangeability.

□ The largest experimentally derived human protein interaction network so far, termed BioPlex 2.0, has been built
>> http://go.nature.com/2qDYrMD


□ Parallel replica dynamics method for bistable stochastic reaction networks: simulation and sensitivity analysis:
>> https://arxiv.org/pdf/1705.06807.pdf
they briefly reproduce the formula for the relative entropy and the path space FIM, in the context of stochastic reaction networks i.e., continuous time jump Markov processes.

□ Inferring Functional Neural Connectivity With Deep Residual Convolutional Networks:
>> http://biorxiv.org/content/early/2017/05/22/141010
The model was trained using a cross-entropy loss function based on proper binary classification of each cell pair’s connectivity. Future work should explore a larger space of layer topology and hyperparameters in order to test the limits of classification efficacy.
□ Direct determination of diploid genome sequences:
>> https://community.10xgenomics.com/t5/10x-Blog/Direct-determination-of-diploid-genome-sequences/ba-p/427
Supernova is a ‘pushbutton’ algorithm -- requires no data processing or user-tuning. Supernova assembler uses a single data type, Linked-Reads, which are sequenced on standard illumina platforms.
□ SiGNet: A signaling network data simulator to enable signaling network inference:
>> http://journals.plos.org/plosone/article/file?id=10.1371/journal.pone.0177701&type=printable
The SiGNet algorithm is based on the understanding of protein behavior, in contrast to similar tools developed for transcriptional networks, which are designed to mimic the dynamics of transcription factors and their target genes.


□ Poincaré Embeddings for Learning Hierarchical Representations:
>> https://arxiv.org/pdf/1705.08039.pdf
Poincaré embeddings enable parsimonious representations whats allows us to learn high-quality embeddings of large-scale taxonomies. prediction results indicate that hyperbolic geometry can introduce an important structural bias for the embedding of complex symbolic data. Poincaré ball is a conformal model of hyperbolic space, angles btwn adjacent vectors are identical to their angles in the Euclidean space. compute embeddings not in Euclidean but in hyperbolic space, i.e., space with constant negative curvature. results for predicting lexical entailment suggest that the hierarchy in the embedding space corresponds well to the underlying semantics.
□ Topological dimension tunes activity patterns in hierarchical modular network models:
>> https://arxiv.org/pdf/1705.08145.pdf
the connectivity strength α controls the network fractal-like structure and shown its proportionality to the topological dimension of a HMN. A direct dependence of λc on D ensures that, being HMNs finite dimensional, the epidemic threshold never vanishes. in the D → ∞ limit, λc ∼ 1/α predicts a vanishing epidemic threshold, recovering the well- known quenched mean field result for SF networks, which are intrinsically infinite dimensional.
□ Bayesian selection of grammar productions for the language of thought:
>> http://biorxiv.org/content/biorxiv/early/2017/05/24/141358.full.pdf
This relationship between the complexity KGeo and the probability PGeo defined for finite sequences in the language of geometry, matches the theoretical prediction for infinite sequences in universal languages described in the Coding Theorem.
□ SRGAP2 and the gradual evolution of the modern human language faculty:
>> http://biorxiv.org/content/biorxiv/early/2017/05/28/143248.full.pdf
achieving a positive effect (establishment of a vocal learning circuit) by inhibiting inhibitors or suppressing the activity of suppressors, appear to have been a common strategy in the evolution of our lineage and our cognitive phenotype.


□ 『Basic Category Theory (ベーシック圏論) by Tom Leinster』
>> https://arxiv.org/pdf/1612.09375.pdf
The most important concept in this book is that of universal property, adjoint functors, representable functors, and limits. In some informal sense, the isomorphism between a finite-dimensional vector space and its double dual is ‘natural’ or ‘canonical’. In contrast, to specify an isomorphism between V and its single dual V∗, we need to make an arbitrary choice of basis, and the isomorphism really does depend on the basis that we choose.
□ An Experiment in Learning the Language of Sequence Motifs: Sequence Logos vs. Finite-State Machines⋆:
>> http://biorxiv.org/content/biorxiv/early/2017/05/27/143024.full.pdf
A modified version of the Evidence-Driven State Merging (EDSM) heuristic is used to reduce the number of states as finite state machines (FSMs) grow too quickly as a function of the number of sequences to reveal any useful structure.
□ Jupyter and Galaxy integration: Easing entry barriers into complex data analyses for biomedical researchers:
>> http://journals.plos.org/ploscompbiol/article?id=10.1371/journal.pcbi.1005425
a hybrid platform combining common analysis pathways with the ability to explore data interactively. Galaxy's power is leveraged for mapping & processing of hundreds of datasets, & Jupyter is used for the final interpretation & replication.

□ Neural-Symbolic Machine Learning for Retrosynthesis and Reaction Prediction:
>> http://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1002/chem.201605499/full
deep neural networks can learn to resolve reactivity conflicts and to prioritize the most suitable transformation rules. The neural symbolic system looks at the query molecule(s) once to calculate the fingerprint, then runs the neural network to determine the 20 most relevant rules, which are subsequently applied.
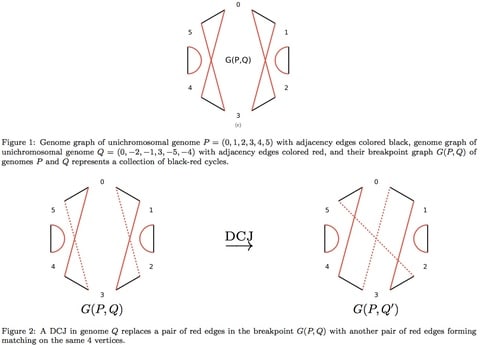
□ Estimation of the True Evolutionary Distance under the Fragile Breakage Model∗:
>> https://arxiv.org/pdf/1510.08002v2.pdf
the random breakage model, has recently been refuted in favor of the more rigorous fragile breakage model postulating that only certain “fragile” genomic regions are prone to rearrangements.
□ Doubly Stochastic Variational Inference for Deep Gaussian Processes:
>> https://arxiv.org/pdf/1705.08933.pdf
using a linear mean function for the high dimensional datasets but left this mean function fixed, as to optimise the parameters would go against the non-parametric paradigm.


□ SpatialDE - Identification of spatially variable genes:
>> http://biorxiv.org/content/biorxiv/early/2017/05/28/143321.full.pdf
Alternative spatial covariance models considered by SpatialDE: no spatial effect, general spatial, periodic spatial patterns & linear trends. SpatialIDE can be used to define distinct spatial patterns of genes, using clustering combined w/ the spatial Gaussian Process framework.
□ Neural networks for solving differential equations: deep networks to solve ODEs and PDEs.
>> https://becominghuman.ai/neural-networks-for-solving-differential-equations-fa230ac5e04c
Autograd allows to take derivatives of any order of particular functions very easily and doesn’t require to mess with epsilon in finite difference approach or to type large formulas for symbolic differentiation software.
net_out_jacobian = jacobian(neural_network_x)(input_point)
net_out_hessian = jacobian(jacobian(neural_network_x))(input_point)

□ SCENIC: Single-cell regulatory network inference and clustering:
>> http://biorxiv.org/content/biorxiv/early/2017/05/31/144501.full.pdf
SCENIC is the first method to analyze scRNA-seq data using a network-centric, rather than cell-centric approach. SCENIC also provide GRNboost, implemented on Spark, as scalable alternative to build the co-expression network.

□ A Model-Free Approach For Detecting Genomic Regions Of Deep Divergence Using The Distribution Of Haplotype Distances
>> http://biorxiv.org/content/early/2017/05/31/144394
HaploDistScan identify novel regions of interest in the Darwin’s finch genome and propose a plausible, data-driven evolutionary history for each novel locus individually and has the power to detect signals of deep divergence.

□ Nontrivial Critical Fixed Point for Replica-Symmetry-Breaking Transitions: Breaking glass in infinite dimensions:
>> https://journals.aps.org/prl/abstract/10.1103/PhysRevLett.118.215701
Consequently, as has been observed for the Abelian gauge theory w/ background fields, Borel-summability depends on the ratio of 2 couplings, as encoded in the saddle-point solution to the classical equations of motion for replicons. the mathematics behind glasses and other disordered systems is actually much easier to solve by assuming that these materials exist in a hypothetical infinite-dimensional universe.


□ Deciphering Molecular Cascades in a Novel Acclimatization Strategy for Rapid Ascent to High Altitude:
>> http://biorxiv.org/content/biorxiv/early/2017/06/02/145342.full.pdf
This study may therefore stand as a proof of concept to translate the objective of rapid acclimatization without compromising the safety and performance of an organism during extreme hypobaric hypoxia exposure.

□ Deep Learning: A Bayesian Perspective:
>> https://arxiv.org/pdf/1706.00473.pdf
Deep predictors are regularized maximum a posteriori (MAP) estimators. Langevin diffusion MCMC, proximal MCMC and Hamiltonian Monte Carlo (HMC) can exploit the derivatives as well as Hessian information.
□ base calling and RNN training tools, nascent consensus calling, have been open sourced, as-is, no warranties, wip.
>> https://github.com/nanoporetech

□ A deep boosting based approach for capturing the sequence binding preferences of RBPs from CLIP-seq data:
>> https://academic.oup.com/nar/article/3858203/A-deep-boosting-based-approach-for-capturing-the
The hyperparameters in the deep boosting framework were determined using an independent dataset. using the weighted decision trees resulting from the deep boosting algorithm to evaluate the relative importance of each encoded feature.










