























帯状疱疹ワクチン接種後にアナフィラキシー反応が起こった患者が、米国南東部でダニに刺された後の牛肉や豚肉のアレルギーの原因として知られるアルファ・ガルに感作していたことで、これらに感作している人は、ゼラチンや他の家畜由来製品含有のワクチンにアレルギー反応を示すという機序を報告している2017年のレター
To the Editor: In the Southeastern United States galactose-a-1,3-galactose(alpha-gal) sensitivity has emerged as a cause of red meat allergy that is causally linked to bites from the lone star tick.1 Alpha-galsensitivity often presents with delayed anaphylaxis after con-sumption of red meat, with lesser degrees of reactivity to milkand gelatin. Gelatin and other nonprimate mammal–derived products are common excipient ingredients in several vaccines,2,3andit has been postulated that patients with alpha-gal allergy mightreact to these vaccines.4 A patient in our clinic with a documented history of red meat allergy since November 2008 required emergency department treatment and epinephrine administration on receipt of live
https://www.jacionline.org/article/S0091-6749(00)68940-6/fulltext
若かりし頃の中山先生の論文
MMRワクチンに含まれるゼラチンが原因でアナフィラキシー反応が発症する問題を、ウシ由来ゼラチンから、加水分解したブタ由来ゼラチンに変更して、アナフィラキシー反応が顕著に減少したという報告。
Anaphylactic reactions after administration of measles, mumps, and rubella combined vaccine were first identified as gelatin allergy by Kelso et al.1 Beginning in 1993, anaphylactic reactions were increasingly reported after administration with gelatin-containing vaccines in Japan.2, 3, 4 IgE antibodies against gelatin were detected most frequently from patients with anaphylactic reactions and less frequently from those with urticarial eruptions.4 We analyzed the prior immunization history of acellular pertussis vaccine combined with diphtheria and tetanus toxoids (DTaP) among patients with gelatin allergy and suggested that the gelatin-containing DTaP may have a causal relationship to the development of gelatin allergy.4 Among 6 manufacturers of DTaP in Japan, two have never used gelatin in the production vaccine. The remaining 4 manufacturers no longer use gelatin, and since February 1999, all DTaPs used in Japan are free of gelatin.
The current measles vaccine contains human serum albumin, gelatin, or both as a stabilizer. Kitasato has chosen to produce live attenuated vaccines by using gelatin as a stabilizer to avoid the potential risk of pathogenic contamination in human serum albumin. Concern over gelatin allergy, however, led Kitasato to change the gelatin from native bovine gelatin to hydrolyzed modified porcine gelatin (Prionex; Pentapharm Corp) in 1998. Prionex gelatin, porcine skin collagen hydrolyzed in the low pH solution and treated at 145°C for 1 hour, showed lower binding activity to IgE antibodies against gelatin (data not shown). Measles and mumps monovalent vaccines with Prionex were introduced in September 1998.
We analyzed the postmarketing clinical adverse reactions before (June 1994-August 1998) and after the introduction of vaccines with Prionex (September 1998-December 1999). The results of the number of reported patients with allergic reactions are shown in Table I.
子宮頸がんワクチンの抗原を開発したZhouとFrazerによる1993年の論文
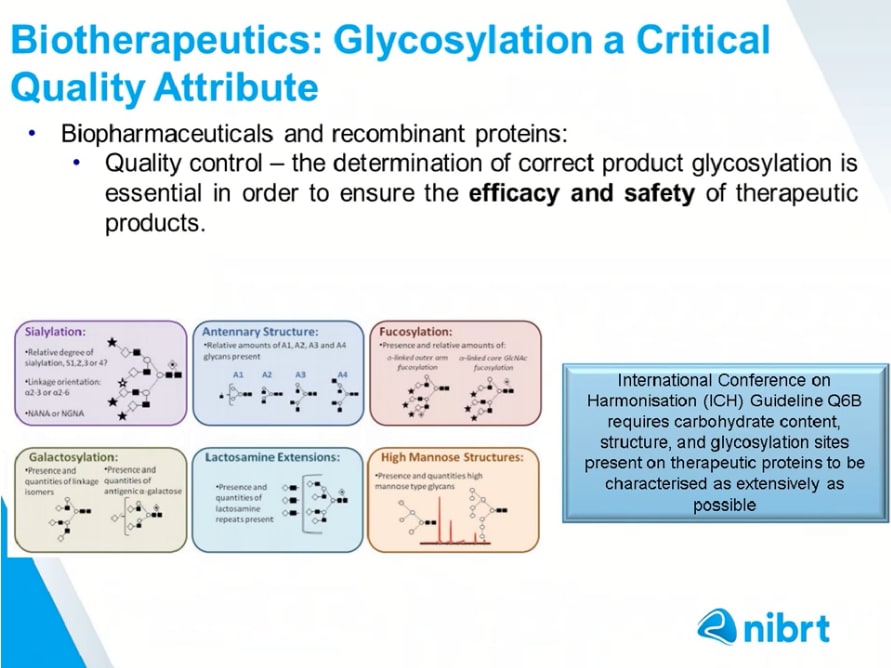
抗原のL1タンパク質の糖化についての考察
タンパク質の発現系として、CV-1細胞(サルの腎臓由来)とHaCaT細胞(ヒトの表皮角化細胞由来)で行ったもの

実際に使用されたワクチンの発現系は、酵母(ガーダシル)と昆虫細胞(サーバリックス)であった
糖化(glycosylation)は、哺乳動物細胞に比べて、酵母や昆虫細胞で発現したものは、性質が悪くなる
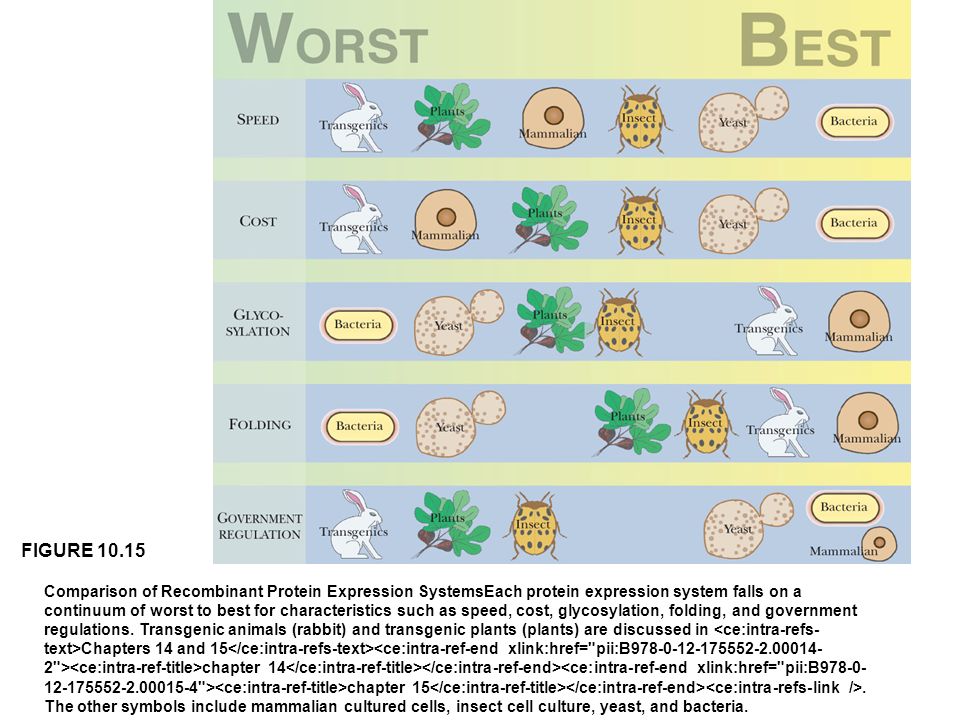
例えば、C型肝炎ワクチンの抗原を、昆虫細胞で作ると、哺乳動物細胞で作るときに比べて抗原性が強くなるという報告がある。
Here, we report that a soluble form of HCV E2 (sE2) produced in insect cells possesses different glycosylation patterns and is more immunogenic, as evidenced by the induction of higher titers of broadly neutralizing antibodies (bNAbs) against cell culture-derived HCV (HCVcc) harboring structural proteins from a diverse array of HCV genotypes.
(J Virol. 2016 Nov 14;90(23):10486-10498.)
糖化が異なることで抗原性が変わるということは、糖化した部分がエピトープになっているということ
では、こうやってヒト以外で発現した抗原にたいする抗体が、果たして、実際にヒトを介して感染した病原体に有効なのかどうか。
基礎研究に従事するリウマチ膠原病内科医の先生のサイト
自己免疫疾患に対する糖鎖修飾治療という新たなフィールド