EP4315694(ERICSSON TELEFON AB L M [SE])
TECHNICAL FIELD
【技術分野】
【0001】
The present invention generally relates to wireless communication networks, and more specifically
本発明は、一般的に、無線通信ネットワークに関連し、より具体的には、
to techniques for prioritization between multiple types (or channels) of data that are available for transmission by a user equipment (UE) during one of a plurality of occasions in which the UE has been granted transmission resources by a wireless network.
無線ネットワークによりUEに送信リソースが許可された、複数の機会のうちの1つの間に、User Equipment(UE)による送信が可能なデータの複数のタイプ間の優先付けのための技術に関連する。
BACKGROUND
【背景技術】
【0002】
Currently the fifth generation (“5G”) of cellular systems, also referred to as New Radio (NR), is being standardized within the Third-Generation Partnership Project (3GPP).
現在、セルラシステムの第5世代(5G)(New Radio(NR)とも呼ばれる)が第3世代パートナーシッププロジェクト(3GPP)内で標準化されている。
NR is developed for maximum flexibility to support multiple and substantially different use cases.
NRは、複数の実質的に異なるユースケースをサポートするための最大限の柔軟性のために開発される。
These include enhanced mobile broadband (eMBB), machine type communications (MTC), ultra-reliable low latency communications (URLLC), side-link device-to-device (D2D), and several other use cases.
これらは、拡張モバイルブロードバンド(eMBB)、マシンタイプ通信(MTC)、超高信頼低遅延通信(URLLC)、サイドリンクデバイスツーデバイス(D2D)及びいくつかの他のユースケースを含む。
NR was initially specified in 3GPP Release 15 (Rel-15) and continues to evolve through subsequent releases, such as Rel-16 and Rel-17.
NRは、3GPPリリース15(Rel-15)において最初に規定され、Rel-16及びRel-17等のその後のリリースを通して進化し続けている。
5G/NR technology shares many similarities with fourth-generation Long-Term Evolution (LTE).
【0003】
5G/NR技術は、第4世代Long-Term Evolution(LTE)と多くの類似点を共有する。
For example, NR uses CP-OFDM (Cyclic Prefix Orthogonal Frequency Division Multiplexing) in the downlink (DL) from network to user equipment (UE), and both CP-OFDM and DFT-spread OFDM (DFT-S-OFDM) in the uplink (UL) from UE to network.
例えば、NRは、ネットワークからユーザ機器(UE)へのダウンリンク(DL)におけるCP-OFDM(Cyclic Prefix Orthogonal Frequency Division Multiplexing)や、UEからネットワークへのアップリンク(UL)におけるCP-OFDMとDFT-spread OFDM(DFT-S-OFDM)の両方を使用する。
As another example, NR DL and UL time-domain physical resources are organized into equal-sized 1-ms subframes.
他の例として、NR DL及びULの時間領域物理リソースは、同じサイズの1msサブフレームに編成される。
A subframe is further divided into multiple slots of equal duration, with each slot including multiple OFDM-based symbols.
サブフレームは、同じ期間の複数のスロットにさらに分割され、各スロットは複数のOFDMベースのシンボルを含む。
However, time-frequency resources can be configured much more flexibly for an NR cell than for an LTE cell.
しかし、時間領域のリソースは、LTEセルよりもNRセルの方がはるかに柔軟に設定されうる。
For example, rather than a fixed 15-kHz OFDM sub-carrier spacing (SCS) as in LTE, NR SCS can range from 15 to 240 kHz, with even greater SCS considered for future NR releases.
例えば、LTEのように固定の15kHz OFDMサブキャリア間隔(SCS)ではなく、NR SCSの範囲は、15から240kHzであり、将来のNRのリリースではさらに大きなSCSが検討される。
In addition to providing coverage via cells as in LTE, NR networks also provide coverage via “beams.”
【0004】
LTEのように複数のセルを介したカバレッジの提供に加えて、NRネットワークは、"ビーム"を介したカバレッジも提供する。
In general, a downlink (DL, i.e., network to UE) “beam” is a coverage area of a network-transmitted reference signal (RS) that may be measured or monitored by a UE.
一般的に、ダウンリンク(DL、例えば、ネットワークからUEへ)"ビーム"は、UEにより測定又は監視されうるネットワーク送信参照信号(RS)のカバレッジエリアである。
In NR, for example, RS can include any of the following: synchronization signal/PBCH block (SSB), channel state information RS (CSI-RS), tertiary reference signals (or any other sync signal), positioning RS (PRS), demodulation RS (DMRS), phase-tracking reference signals (PTRS), etc.
NRでは、例えば、RSは、以下のいずれかを含めることができる:同期信号/PBCHブロック(SSB)、チャネル状態情報RS(CSI-RS)、三次参照信号(又は任意の他の同期信号)、ポジショニングRS(PRS)、復調RS(DMRS)、位相トラッキング参照信号(PTRS)等。
In general, SSB is available to all UEs regardless of the state of their connection with the network, while other RS ( e.g CSI-RS, DM-RS, PTRS) are associated with specific UEs that have a network connection.
一般的に、SSBは、ネットワークとの接続状態に関わらず、全てのUEに利用可能であり、他のRS(例えば、CSI-RS、DM-RS、PTRS)は、ネットワーク接続のある特定のUEに関連付けられる。
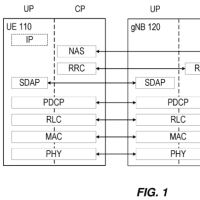
Figure 1 shows an exemplary configuration of NR user plane (UP) and control plane (CP) protocol stacks between a UE, a gNodeB (gNB, e.g., base station), and an access and mobility management function (AMF) in the 5G core network (5GC).
【0005】
図1は、5Gコアネットワーク(5GC)におけるUE、gNodeB(gNB、例えばベースステーション)、及び、アクセス・移動管理機能(AMF)の間におけるNRユーザプレーン(UP)及び制御プレーン(CP)プロトコルスタックの例示的な構成を示す。
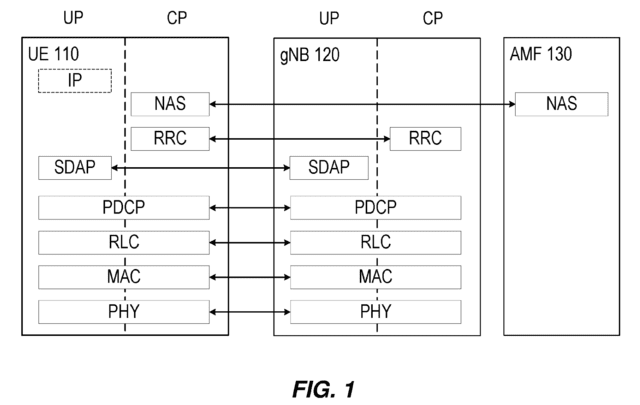
Physical (PHY), Medium Access Control (MAC), Radio Link Control (RLC), and Packet Data Convergence Protocol (PDCP) layers between the UE and the gNB are common to UP and CP.
UEとgNBとの間における、Physical(PHY)、Medium Access Control(MAC)、Radio Link Control(RLC)、及び、Packet Data Convergence Protorol(PDCP)レイヤは、UP及びCPで共通である。
The PDCP layer provides ciphering/deciphering, integrity protection, sequence numbering, reordering, and duplicate detection for CP and UP.
PDCPレイヤは、CP及びUPに対して、暗号化/復号、完全性の保護、シーケンス番号、並べ替え、及び、重複検出を提供する。
/////////
In contrast, a transmission without an explicit grant/assignment is typically configured to occur during occasions with a defined periodicity.
【0012】
それに対して、明示的な許可/割当てのない送信は、定義された周期性のある機会(occasion)の間に行われるように通常は構成される。
Given a periodic and/or recurring UL grant and/or DL assignment, the UE can then initiate a data transmission and/or receive data according to a predefined configuration.
定期的及び/又は反復的なUL許可及び/又はDL割当てが与えられると、UEは、予め定められた設定に従って、データ送信の開始及び/又はデータの受信を行いうる。
Such transmissions can be referred to as semi-persistent scheduling (SPS, for DL), configured grant (CG, for UL), or grant-free transmissions.
そのような送信は、準永続的スケジューリング(SPS、DL向け)、設定許可(configured grant)(CG、UL向け)又は、グラント・フリー送信と呼ばれうる。
////////////
There can be one or more HARQ processes in the HARQ process pool assigned to each CG configuration.
【0087】
HARQプロセスプールにおける1つ以上のHARQプロセスが、各CG設定に割り当てられうる。
In particular, each CG can be configured with parameters nrofllARQ-Processes and harq-ProcID-Offset (shown in Figure 7)
特に、各CGは、nrofHARQ-Processesとharq-ProcID-Offset(図7に示される)のパラメータが設定されてもよく、
so that the UE can select a HARQ process ID within \harq-procID-offset, {harq-procID-offset + nrofllARQ-Processes - 1)] for transmission during an occasion of the CG.
UEは、CGの機会中の送信のために、[harq-procID-offset、...、(harq-procID-offset+nrofHARQ-Processes -1)]の中からHARQプロセスIDを選択しうる。
HARQ processes can also be shared between CG configurations,
HARQプロセスは、また、複数のCG設定間で共有されうる。
which can increase flexibility and avoid depletion of limited HARQ process space for the UE.
これにより、柔軟性が向上し、UEにとって限られたHARQプロセス空間の枯渇を避けうる。
Each CG configuration also includes CGT and CGRT settings (shown in Figure 7).
各CG設定は、CGT及びCGRT設定も含む(図7に示される)。