US20150017868(対応日本語公報)
(Abstract)
"A hot melt adhesive composed of an ethylene vinyl acetate copolymer, a hydrogenated styrenic block copolymer, a tackifying resin, and a liquid plasticizer. The preferred ethylene vinyl acetate copolymer has a vinyl acetate content between 8 and 28 percent by weight, and the preferred hydrogenated styrenic block copolymer is a styrene-ethylene-butylene-styrene having about 30% styrene content and essentially no diblock. The hot melt gives excellent peel strength when used as a construction adhesive for disposable nonwoven articles. It can also be formulated(配合)to exhibit very low bleed through and blocking characteristics when used on low basis weight nonwoven fabrics."
US20160046807(対応日本語公報)
"1. A polyamide composition produced by a process comprising the step of compounding(配合)a mixture comprising a polyamide, an olefin-maleic anhydride copolymer, and an impact modifier."
US9102571(対応日本語公報)
"7. The method of claim 1, wherein forming the at least one prepregged composite material comprises formulating(配合)the pre-ceramic matrix slurry to impart the prepregged composite material with sufficient rigidity to be cut by the advanced fiber placement apparatus following placement of at least a portion of the at least one prepregged composite material over the at least one surface of the tool and with sufficient tackiness to adhere to the at least one surface of the tool."
US20140057105(対応日本語公報)
(Abstract)
"Various embodiments of the present invention relate to surface enhanced pulp fibers, various products incorporating(配合)surface enhanced pulp fibers, and methods and systems for producing surface enhanced pulp fibers. Various embodiments of surface enhanced pulp fibers have significantly increased surface areas compared to conventional refined fibers while advantageously minimizing reductions in length following refinement. The surface enhanced pulp fibers can be incorporated into(配合)a number of products that might benefit from such properties including, for example, paper products, paperboard products, fiber cement boards, fiber reinforced plastics, fluff pulps, hydrogels, cellulose acetate products, and carboxymethyl cellulose products. In some embodiments, a plurality of surface enhanced pulp fibers have a length weighted average fiber length of at least about 0.3 millimeters and an average hydrodynamic specific surface area of at least about 10 square meters per gram, wherein the number of surface enhanced pulp fibers is at least 12,000 fibers/milligram on an oven-dry basis."
US20130149926(対応日本語公報)
"19. The method of claim 15 further including forming the solution by diluting the binder with water and compounding(配合)a single flame retardant with the binder and water mixture."
US20140220198(対応日本語公報)
"12. A process of manufacturing an ultrasonically-treated nutritional formulation(栄養製剤), the process comprising: combining(配合)a protein, a carbohydrate, a lipid, a binder, and water to form a slurry; subjecting the slurry to high power ultrasound; and extruding the slurry to produce the ultrasonically-treated nutritional formulation."
US7462662(対応日本語公報)
(Abstract)
"Improved fire-retarded properties can be imparted to fiber reinforced polycarbonate resin composition by incorporating into(配合)the polycarbonate an effective flame-retardant amount of a combination of perfluoroalkane sulfonate and talc."
"19. A method to increase the flame retardant property of a polycarbonate composition containing an amount of at least a perfluoroalkane sulfonate flame retardant component, to render the composition a flame rating of at least V-0 in the Underwriter's Laboratory UL-94 protocol when measured on a test specimen of about 0.062 inch by about 0.5 inch by about 5 inch dimensions, said method comprises blending into(配合)said composition an effective flame-retardant amount talc; wherein the polycarbonate composition consists essentially of the polycarbonate resin, the perfluoroalkane sulfonate flame retardant and the talc."
"Because of their strength and clarity, polycarbonate resins have a great many significant commercial applications. Unfortunately, polycarbonate resins are inherently flammable and can drip hot molten material causing nearby materials to catch fire as well. Thus, in a number of applications employing polycarbonate blends, it may be desirable to include(配合)additives which retard the flammability of the material and/or which reduce dripping. The challenge is to identify additives which accomplish this purpose without compromising the desirable properties of strength and clarity, without introducing new problems (such as the potential environmental problems associated with halogenated additives) and without prohibitively increasing the price."
"Achieving flame-retardant resin properties sufficient for obtaining an Underwriter's Laboratories listing is a prerequisite for many commercial applications of thermoplastic resins. To achieve listings of UL94 V-1 and or UL94 V-0 at the desired thicknesses (.ltoreq.2.5 mm), several known flame retardants can be used. But in addition to adding cost, they have other disadvantages compared to non-flame retarded compositions. For example, the use of brominated compounds would preclude a resin from use in applications where conformance with TCO'99 guidelines (non-halogen) is desired. Other regulations or customer preferences may preclude the use of elemental (red) phosphorous or organic phosphates and phosphites. In addition, organic phosphates and phosphites reduce the deflection temperature under load (heat distortion temperature) of polycarbonate (PC)-resins and--because they are low molecular weight compounds--can form undesirable deposits on injection molding tools or the part surface, which in turn can lead to chemical stress cracking. Melamine cyanurates or inorganic hydrates (like aluminum trihydrate--ATH) cannot be incorporated(配合)effectively into resins requiring high processing temperatures due to the onset of their own thermal decomposition in that temperature range and typically reduce impact resistance significantly due to their particulate nature. These constraints are even more important in fiber reinforced composites, because these typically require larger amounts of flame retardant or more effective/costly ones to achieve UL94 V-1 or even UL94 V-0 listings.
Among the additives which are widely used commercially in fire-retarded polycarbonate resin compositions are organic salts, particularly sulfonic acid salts. Particular examples of these salts are perfluoroalkane sulfonates, such as potassium perfluorobutane sulfonate ("PFBS", also known as "Rimar salt" and potassium diphenylsulfone sulfonate ("KSS"), which may yield haze free compositions when blended with(配合)polycarbonate resin. The use of perfluoroalkane sulfonates in polycarbonate resins is described in U.S. Pat. No. 3,775,367. However, the benefits which can be obtained using these materials alone are limited and indeed additional additives are generally included."
"Applicants have found that(見出した、知見を得た)the incorporation(配合)of an effective, flame-retardant amount of talc surprisingly reduces the flame-out time of a polycarbonate composition, even without any flame retardant component being present."
最新の画像[もっと見る]
-
 中抜き(半導体製造)
1日前
中抜き(半導体製造)
1日前
-
 西瓜は神
3日前
西瓜は神
3日前
-
 素線
5日前
素線
5日前
-
 採れたて!豊作!
6日前
採れたて!豊作!
6日前
-
 採れたて!豊作!
6日前
採れたて!豊作!
6日前
-
 採れたて!豊作!
6日前
採れたて!豊作!
6日前
-
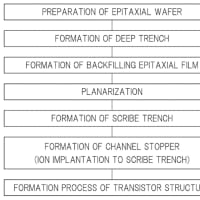 ステップに示すように
1週間前
ステップに示すように
1週間前
-
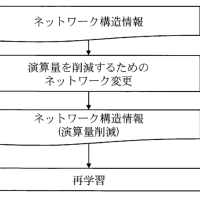 ステップに示すように
1週間前
ステップに示すように
1週間前
-
 ステップに示すように
1週間前
ステップに示すように
1週間前
-
 ステップに示すように
1週間前
ステップに示すように
1週間前
















※コメント投稿者のブログIDはブログ作成者のみに通知されます