NOVEMBER 2017 TOP500 LIST
The fiftieth TOP500 list of the fastest supercomputers in the world has China overtaking the US in the total number of ranked systems by a margin of 202 to 143. It is the largest number of supercomputers China has ever claimed on the TOP500 ranking, with the US presence shrinking to its lowest level since the list’s inception 25 years ago.
Just six months ago, the US led with 169 systems, with China coming in at 160. Despite the reversal of fortunes, the 143 systems claimed by the US gives them a solid second place finish, with Japan in third place with 35, followed by Germany with 20, France with 18, and the UK with 15.
China has also overtaken the US in aggregate performance as well. The Asian superpower now claims 35.4 percent of the TOP500 flops, with the US in second place with 29.6 percent.
The top 10 systems remain largely unchanged since the June 2017 list, with a couple of notable exceptions.
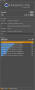
Sunway TaihuLight, a system developed by China’s National Research Center of Parallel Computer Engineering & Technology (NRCPC), and installed at the National Supercomputing Center in Wuxi, maintains its number one ranking for the fourth time, with a High Performance Linpack (HPL) mark of 93.01 petaflops.
Tianhe-2 (Milky Way-2), a system developed by China’s National University of Defense Technology (NUDT) and deployed at the National Supercomputer Center in Guangzho, China, is still the number two system at 33.86 petaflops.
Piz Daint, a Cray XC50 system installed at the Swiss National Supercomputing Centre (CSCS) in Lugano, Switzerland, maintains its number three position with 19.59 petaflops, reaffirming its status as the most powerful supercomputer in Europe. Piz Daint was upgraded last year with NVIDIA Tesla P100 GPUs, which more than doubled its HPL performance of 9.77 petaflops.
The new number four system is the upgraded Gyoukou supercomputer, a ZettaScaler-2.2 system deployed at Japan’s Agency for Marine-Earth Science and Technology, which was the home of the Earth Simulator. Gyoukou was able to achieve an HPL result of 19.14 petaflops. using PEZY-SC2 accelerators, along with conventional Intel Xeon processors. The system’s 19,860,000 cores represent the highest level of concurrency ever recorded on the TOP500 rankings of supercomputers.
Titan, a five-year-old Cray XK7 system installed at the Department of Energy’s (DOE) Oak Ridge National Laboratory, and still the largest system in the US, slips down to number five. Its 17.59 petaflops are mainly the result of its NVIDIA K20x GPU accelerators.
Sequoia, an IBM BlueGene/Q system installed at DOE’s Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory, is the number six system on the list with a mark of 17.17 petaflops. It was deployed in 2011.
The new number seven system is Trinity, a Cray XC40 supercomputer operated by Los Alamos National Laboratory and Sandia National Laboratories. It was recently upgraded with Intel “Knights Landing” Xeon Phi processors, which propelled it from 8.10 petaflops six months ago to its current high-water mark of 14.14 petaflops.
Cori, a Cray XC40 supercomputer, installed at the National Energy Research Scientific Computing Center (NERSC), is now the eighth fastest supercomputer in the world. Its 1,630 Intel Xeon "Haswell" processor nodes and 9,300 Intel Xeon Phi 7250 nodes yielded an HPL result of 14.01 petaflops.
At 13.55 petaflops, Oakforest-PACS, a Fujitsu PRIMERGY CX1640 M1 installed at Joint Center for Advanced High Performance Computing in Japan, is the number nine system. It too is powered by Intel “Knights Landing” Xeon Phi processors.
Fujitsu’s K computer installed at the RIKEN Advanced Institute for Computational Science (AICS) in Kobe, Japan, is now the number 10 system at 10.51 petaflops. Its performance is derived from its 88 thousand SPARC64 processor cores linked by Fujitsu’s Tofu interconnect. Despite its tenth-place showing on HPL, the K Computer is the top-ranked system on the High-Performance Conjugate Gradients (HPCG) benchmark.