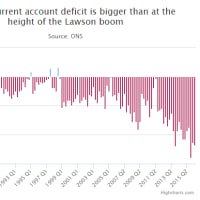
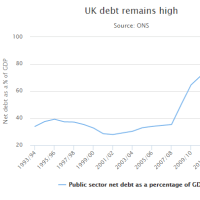
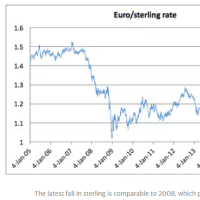
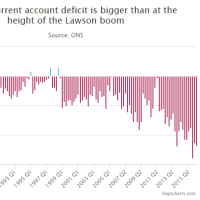
Asia's top banks warn that Chinese capital flight is becoming dangerous
(アジア屈指の銀行が中国の資本逃避が危険になりつつあると警告)
Ambrose Evans-Pritchard
Telegraph: 5 FEBRUARY 2017 • 9:34PM


(アジア屈指の銀行が中国の資本逃避が危険になりつつあると警告)
Ambrose Evans-Pritchard
Telegraph: 5 FEBRUARY 2017 • 9:34PM
China's central bank is running out of ways to stem capital flight and faces a near impossible task trying to manage the fall-out from extreme credit growth, two of Asia's most influential banks have warned.
中国人民銀行は資本逃避阻止の手段を使い尽くしつつあり、極端な信用増加の影響の管理を試みるというほぼ不可能な任務に直面している、とアジアで最も影響力のある銀行が警告しました。
"Defence of the currency by the People's Bank (PBOC) is no longer a viable option," said Eric Robertson, the head of global macro strategy for Standard Chartered.
スタンダード・チャータードのヘッド・オブ・グローバル・マクロ・ストラテジー、エリック・ロバートソン氏は「中国人民銀行の通貨防衛はもう実行可能な選択じゃないね」と言います。
The Asia-focused lender said powerful forces are driving capital out of the country and the picture is fundamentally more disturbing than it was during last year's devaluation panic. This is putting the PBOC in an invidious position as it attempts to deal with festering troubles in the banking system.
アジアに焦点を置くこの銀行によると、強烈な力が中国から資本を追い出しつつあり、様相は基本的に昨年のデバリュエーション・パニックよりも憂慮すべきものだそうです。
これは銀行システムで悪化するトラブルに対処しようとする中国人民銀行を不愉快な立場に置くことになります。
The Institute of International Finance estimates that outflows reached a record $725bn (£581bn) last year and there is little sign of any slowdown despite ever tighter capital controls.
国際金融協会の試算によれば昨年の流出額は史上最高の7,250億ドル(5,810億ポンド)に達したそうで、資本規制の一層の強化にも拘らず減速する兆しは殆どないとのことです。
Mr Robertson said aggressive intervention on the currency markets to slow the fall of the yuan automatically drains liquidity and tightens financial conditions. "They risk doing enormous damage to the onshore banking system," he said.
ロバートソン氏曰く、人民元下落を減速させるための積極的為替介入が、流動性を減らして金融を引き締めているとのこと。
「彼らは国内の銀行システムにとんでもないダメージを与えかねない」と同氏は言いました。
The Japanese bank Nomura issued a parallel alert on China's "incredible five-ball juggling act", warning that East Asia as a whole is sailing into a financial storm. There is a high risk of a region-wide credit crunch escalating into something hard to control.
日本の野村證券は中国の「驚くべき5つボール・ジャグリング」に関する類似したアラートを出し、東アジア全体が金融嵐に突き進んでいると警告しました。
地域全体の信用不足が制御困難なものにエスカレートする高いリスクがあります。
"Asia is likely to be more vulnerable than people think," said Rob Subbaraman, the bank's chief global strategist. The risk is that fund managers could pull their money out "en masse", puncturing the illusion of market liquidity.
「アジアは皆が思っているより弱い可能性が高いね」と同行のチーフ・グローバル・ストラテジスト、ロブ・スバラマン氏は言います。
ファンドマネジャーが「一斉に」資金を引き揚げて市場の流動性のイリュージョンを壊してしまいかねません。
While the PBOC still has $3 trillion of foreign exchange reserves, these bond holdings are hard to deploy in China's internal economy without making matters worse. The country must now pick between poisons.
中国人民銀行には未だ3兆ドルの外貨準備があるものの、これらの債券を中国の国内経済で事態を悪化させることなく使うのは困難です。
この国は今やどちらかの毒を選ばなければならないのです。
The reserves are not as large as they look given the scale of the financial pressures and the structure of the Chinese economy. The ratio of the M2 money supply to reserves has collapsed to a 15-year low and this may prove to be the crucial ratio in a confidence crisis.
金融プレッシャーのスケールや中国経済の構造を考えれば、この外貨準備は見た目ほど巨額ではありません。
M2マネーサプライの準備金に対する比率は15年ぶり最低まで落ち込んでおり、これは信頼性の危機における重要な比率だとわかることになるかもしれません。
Standard Chartered said nobody knows at what point the PBOC will lose its room for manoeuvre but the balancing act is becoming ever harder. "If the reserves are allowed to fall meaningfully below $3 trillion, people will start to worry about reserve adequacy. The markets will grab hold of this," said Mr Robertson.
スタンダード・チャータードによれば、中国人民銀行が余裕を失うポイントは誰にもわからないものの、バランスを取るのは益々困難になりつつあるそうです。
「準備がしっかり3兆ドル以下になるまで減るのを放置すれば、準備金の妥当さについて皆心配し始めるだろうね。市場はこれに付け込むだろう」とロバートソン氏は言いました。
The cautionary language from Standard Chartered is significant. The bank has close ties to China and is a key agent for the country's offshore yuan transactions.
スタンダード・チャータードの注意書きは重大です。
同行は中国と密接な関係を持っている上に、人民元のオフショア取引の主要エージェントです。
The PBOC is tapping on brakes – gently, so far – raising a range of rates last week in a calibrated move to cool the excesses. Economic consultants Capital Economics says it is the first official acknowledgement of stealth tightening that has been under way since November. Until now the PBOC has been quietly dialling down the "quantity" of underlying loan growth, its usual method of micro-managing the cycle.
中国人民銀行はブレーキを踏んで(これまでのところは柔らかく)、先週は過熱を落ち着かせるための調整された動きの中で様々な金利を引き上げました。。
キャピタル・エコノミクスは、11月から進んでいるステルス引き締めの存在を初めて公に認めたと言っています。
これまで、中国人民銀行は基礎的な融資の「量」の伸びを密かに抑えてきました。
景気サイクルを細かく管理するいつもの手段です。
The PBOC is now starting to tighten the more visible "price" of loans as well. "It is only a matter of time before credit growth, a key tailwind behind the economic recovery in 2016, starts to become a drag," said the consultancy.
中国人民銀行は今、より目立つ融資「価格」の引き締めも開始しつつあります。
「2016年の景気回復の背後の主な追い風、信用の伸びが邪魔になり始めるのも時間の問題だ」とキャピタル・エコノミクスは述べています。
Standard Chartered said the great worry is that the Trump administration and the US Congress will pass a "border adjustment tax" on imports, triggering ructions in the global currency markets.
スタンダード・チャータードによれば、大きな懸念材料はトランプ政権と米議会が輸入に対する「国境調整税」を可決して、世界の為替市場に大騒動を引き起こすことだそうです。
Most economists fear such a tax could lead to a dollar spike of 15 to 20 per cent. This would set off an earthquake in a global financial system that has never been more dollarised and carries $10 trillion of offshore dollars with no lender-of-last resort behind it.
殆どのエコノミストは、そのような課税は米ドルを15-20%急上昇させかねないと危惧しています。
このようなことになれば、前例がないほど米ドル化されている上に最後の貸し手不在のオフショア・ドル建て融資が10兆ドルも存在する国際金融システムに激震が走るでしょう。
Mr Robertson said the consequences for China do not bear thinking about. A move of this kind would be a psychological shock for Chinese savers who tend to follow the headline yuan-dollar exchange rate.
ロバートソン氏は、中国にとっての結果は想像に耐えないと言います。
この種の動きは、人民元のヘッドライン為替レートに従う傾向を持つ中国人貯蓄家にとって心理的ショックとなるでしょう。
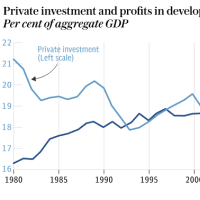
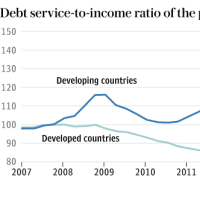
Nomura said much of East Asia is in the late stage of an exhausted credit cycle that has led to endemic mal-investment. The debt service ratio has jumped five-fiold over after the last decade and is now 15 per cent of GDP, exactly where it was at the onset of the Asian financial crisis in 1997 – but on a much bigger scale.
野村證券によれば、東アジアの大半は特有の投資ミスをもたらしてきた終わりかけた信用サイクルの最終段階にあるそうです。
債務返済比率は2010年以降5倍に跳ね上がり、今ではGDPの15%に達しています。
1997年の東アジア金融危機の始まりと正に同じですが、そのスケールは遥かに大きくなっています。
The region is in the eye of the storm, at risk from US monetary tightening and the geopolitical fall-out from a trans-Pacific trade war.
この地域は台風の目に当たり、米金融引き締めと太平洋横断貿易戦争の地政学的影響の危険にさらされています。
"China has reached the point where the rubber hits the road: The problems of property and debt overhangs and keeping zombie companies afloat have become so large that they are bearing down on growth via falling returns on capital and rising debt-servicing costs," said Mr Subbaraman.
「中国は肝心なポイントに至った。不動産と債務の残り物やゾンビ会社を生かしておくことの問題がデカくなり過ぎて、資本に対する利益の減少や債務返済コストの増加を通じて成長の足を引っ張っている」とスバラマン氏は言いました。
"Monetary and fiscal stimulus to achieve unrealistic growth targets is not the answer; they are losing efficacy and risk fuelling more bubbles and misallocating more resources," he said.
「非現実的な成長目標達成のための金融刺激と財政刺激は解決策じゃない。効能は失われつつある上に、更なるバブルを助長したり更にリソースの配分ミスをやらかす危険性がある」とのことです。