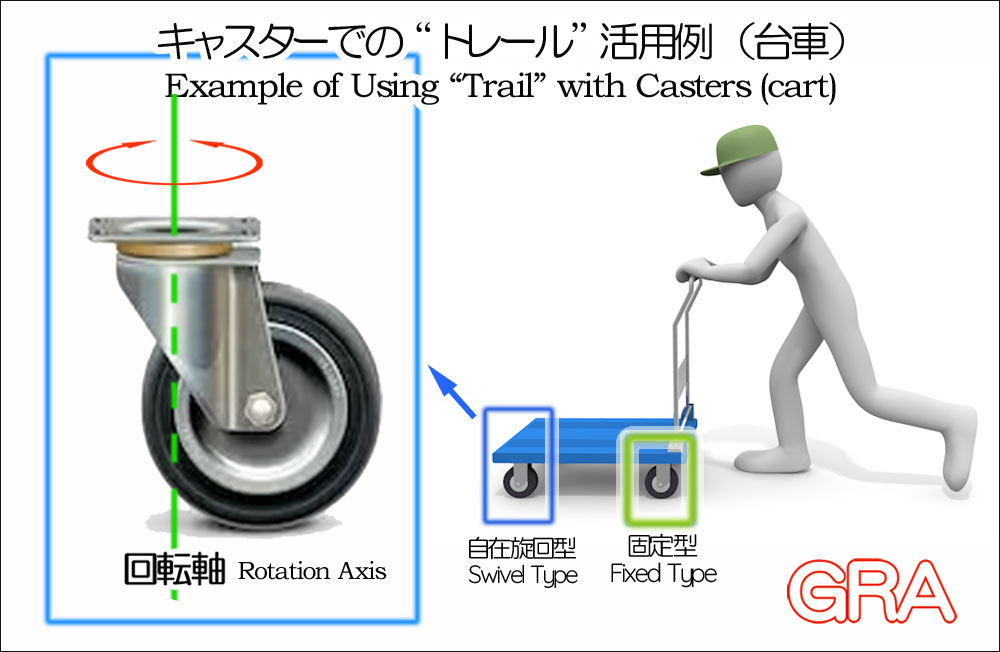
寄せられた質問に詳しく回答する Q&Aコーナーで、記事『フルロックは必要か?』に掲載する詳細な解説の一部の初校が出来ましたので、ここに紹介します。
The first draft of part of the detailed explanation to be published in the Q&A article "Is full lock necessary?" has been completed, so we would like to introduce it here.
キャスター角の理解には注意が必要です。
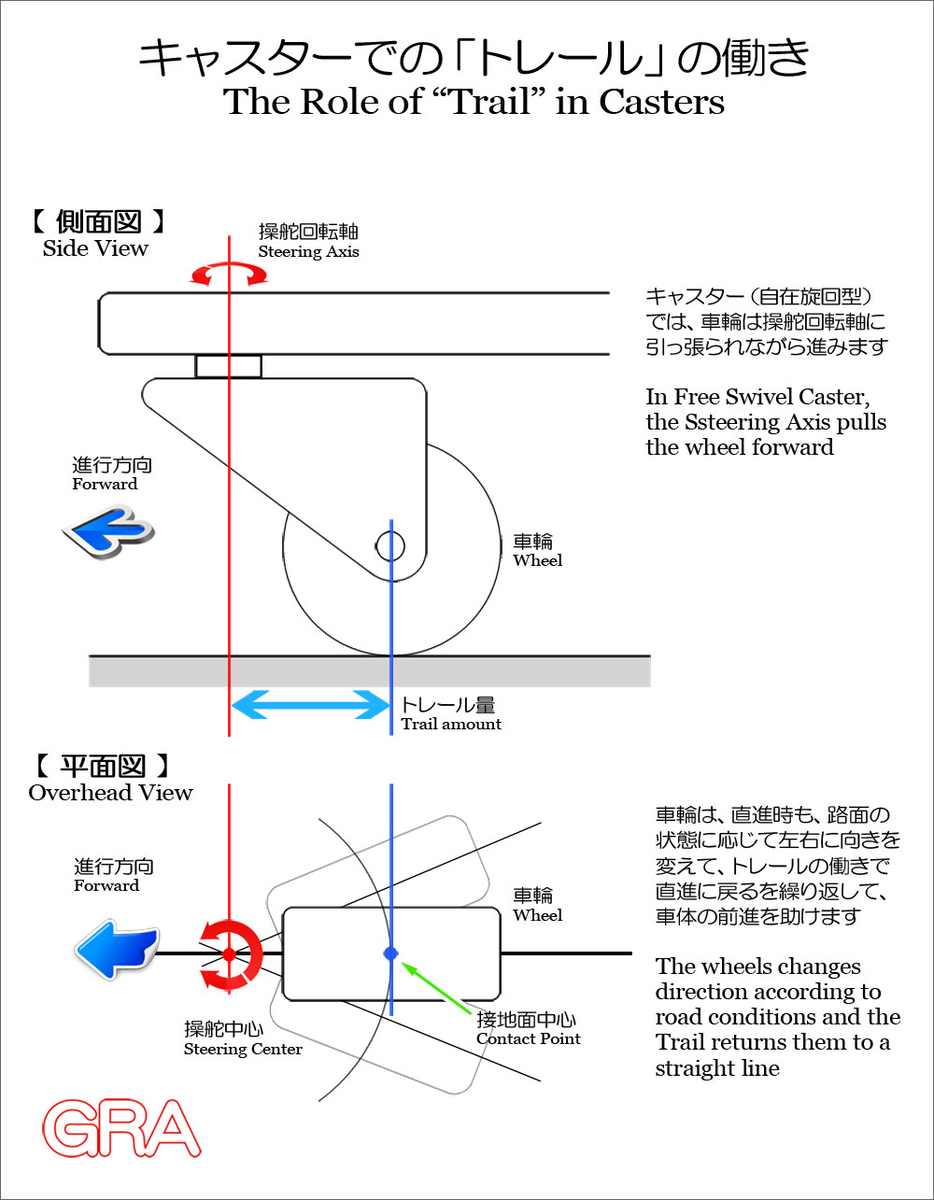
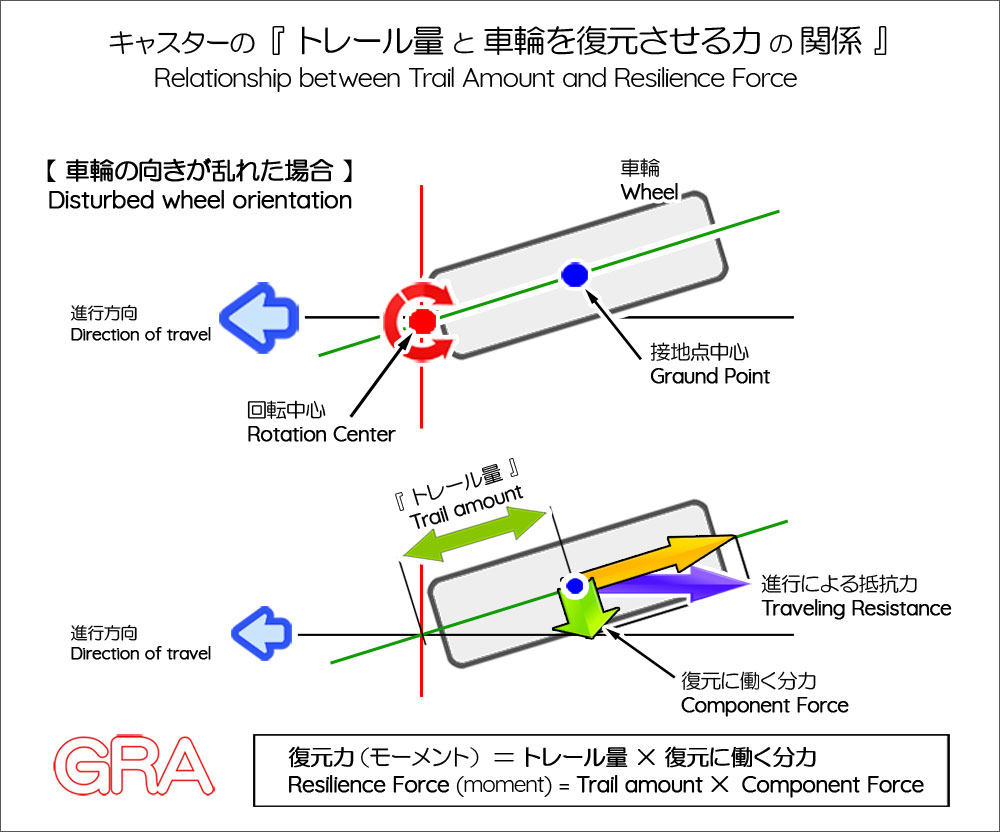
あなたも体験していると思いますが、オートバイと自動車とでは、旋回時の操縦性や特性は全く異なります。それは、旋回の原理や車両構造が基本的に異なるからです。しかし、残念な事に、自動車と同じ理論でオートバイを語る傾向が強く、キャスター角についても、自動車の場合と同様に「直進安定性を高める」と表現される例が多くあります。けれども、それは決して正しい理解とは言えません。オートバイにとってキャスター角は、結果的にトレール量を生み出して直進安定性を得ている面はありますが、本質的には「旋回のきっかけ作り」をする要素であり、直進安定性を乱す要素だからです。
It is important to be careful when understanding caster angle.
As you may have experienced, the maneuverability and characteristics when turning are completely different between motorcycles and cars. This is because the principles of turning and the vehicle structures are fundamentally different. Unfortunately, however, there are many cases where the caster angle of motorcycles, just like that of cars, is described as "improving straight-line stability." However, this is by no means an accurate understanding. For motorcycles, caster angle does ultimately create trail and provide straight-line stability, but in essence it is an element that "creates an opportunity to turn" and disrupts straight-line stability.
自動車とオートバイとで、キャスター角の目的が異なっている事は、それぞれの角度にも表れています。自動車は直進安定性を高める必要があるのですが、キャスター角は 3度から 5度程度で、オートバイの 25度から 30度程度の角度と較べると大幅に小さく、一見、直進安定性が少なく思えます。しかし、直進安定性の為に必要なキャスター角はその程度で充分なのです。一方、オートバイのキャスター角が大きいのは、直進走行から車体を傾けて旋回を始める際、前輪が旋回方向へと向きを変える「キャスターアクション」を獲得する為に必要だったと考えられます。「キャスターアクション」は、下の図で解説している通り、操舵軸(操舵回転軸)よりも 車輪やサスペンション、ハンドル周りのステアリング系の重心点が上にある事に始まります。そして、操舵角が大きくなるにつれて、路面から受けている反力によって、更にその操舵角が大きくなるという少しやっかいな特性も持っています。
The different purposes of caster angle between automobiles and motorcycles are also reflected in their respective angles. Cars need to improve straight-line stability, but the caster angle is about 3 to 5 degrees, which is significantly smaller than the 25 to 30 degrees of motorcycles, but that is enough for straight-line stability. On the other hand, the large caster angle of motorcycles is thought to be necessary to obtain the "caster action" that causes the front wheel to change direction in the direction of the turn when the vehicle starts to lean from a straight line and turn. "Caster action" occurs when the center of gravity of the steering system, such as the wheels and suspension, is higher than the steering axis. Also, as the steering angle increases, the reaction force from the road surface makes the steering angle even larger, which is a bit of a nuisance.
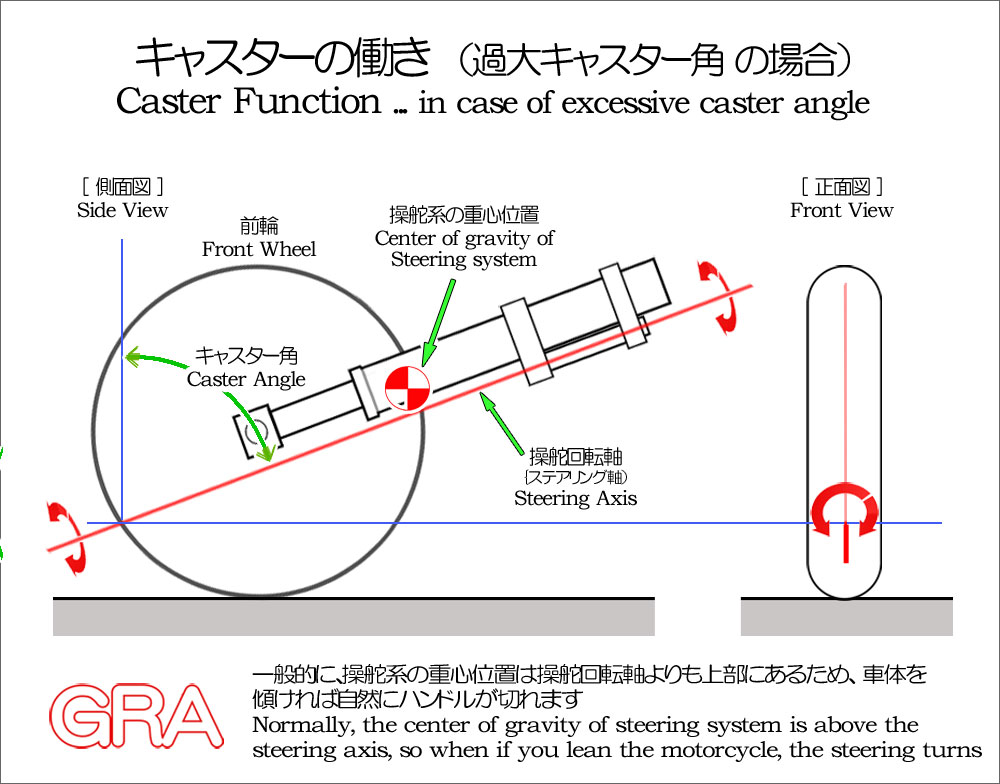
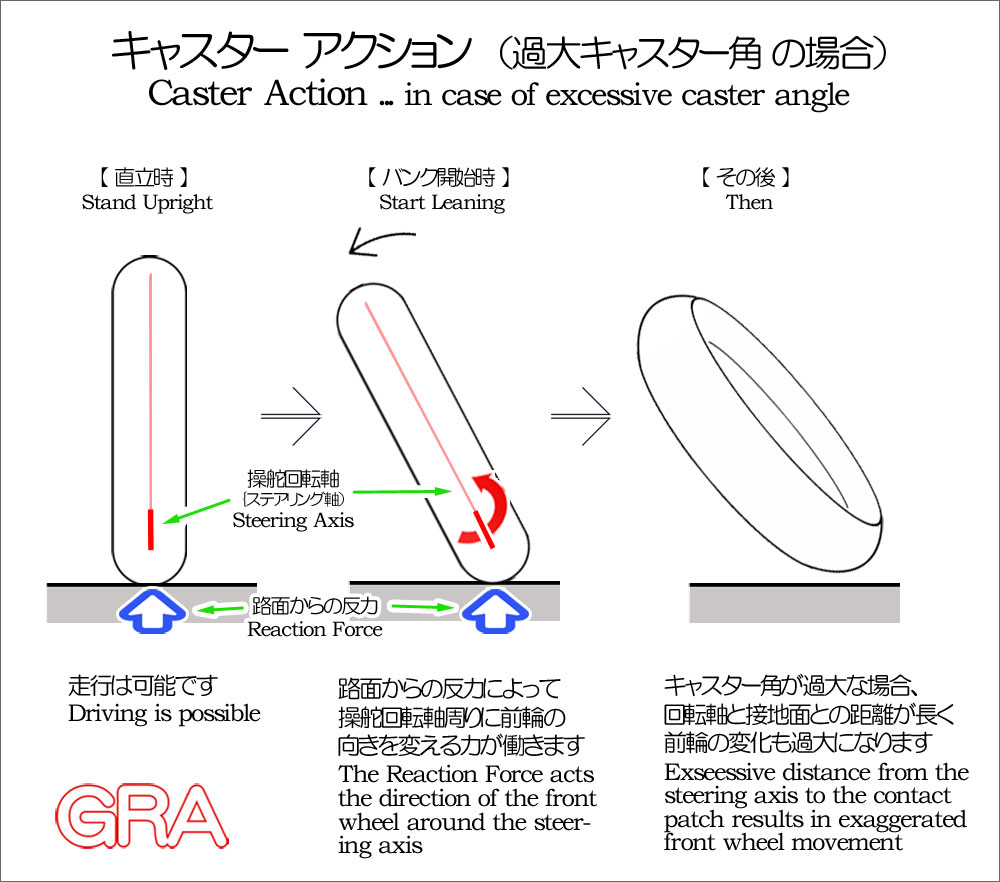
以上の通り、オートバイでは、「キャスターアクション」で旋回を助けると同時に、その弊害と危険性を避ける為に、キャスター角は 30度以内の設定で落ち着いていると考えられます。そして、同時に、一般的なフロントサスペンションであるテレスコピック形式では、路面追従性を高めて、路面の凸凹によるフロントタイヤのグリップ喪失を防ぐ為にも、フロントフォークを後傾する必要があり、現在の様な角度設定になっていると言えます。つまり、オートバイ特有の特性の為に、キャスター角が設定されており、決して直進安定性の為とは言えない事が分かります。そして、仮に、テレスコピック形式以外のサスペンションが普及した際は、当然ですが、現在とは異なるキャスター角設定になる事は充分に考えられます。
As mentioned above, in motorcycles, the caster angle is set to within 30 degrees to help turning with "caster action" while avoiding its disadvantages and dangers. At the same time, in the telescopic type, which is a common front suspension, the front fork needs to be tilted backward to improve road following and prevent the front tire from losing grip due to unevenness in the road surface, so it can be said that the current angle is set. In other words, the caster angle is set due to the characteristics unique to motorcycles, and it can never be said to be for straight-line stability.
*************
なお、自動車が基本の学問・自動車工学では、「キャスターアクション」の定義はオートバイの場合とは異なっているので注意が必要です。自動車の場合のキャスターアクションとは、「走行時、ハンドルを切った際、自動的に直進状態へと戻ろうとする作用であり力の事」を指しています。つまり、自動車の「直進安定性」とは、旋回中にハンドルから手を離すと、操舵輪(主に前輪)が直進状態へと戻る作用であり、それを生み出している要素の一つがキャスター角です。しかし、オートバイでの旋回時には同様の作用は無く、キャスター角の目的が全く異なっている事が理解できるでしょう。
Please note that in automotive engineering, a field based on automobiles, the definition of "caster action" is different from that of motorcycles. In the case of automobiles, caster action refers to the force that automatically returns the car to a straight-line state when the steering wheel is turned while driving. In other words, the "straight-line stability" of an automobile is the action of the steering wheel returning to a straight-line state when the hands are taken off the steering wheel while turning, and one of the factors that creates this is the caster angle. However, there is no similar action when turning on a motorcycle, so you can see that the purpose of the caster angle is completely different.
*************
余談ですが、キャスター角が異常に大きく設定されている例を紹介します。それは、トラックレーサーと呼ばれている、トラック競技やマラソンなどで使用される車椅子です。
As an aside, I will introduce an example where the caster angle is set abnormally large. It is a wheelchair called a track racer, which is used in track events and marathons.
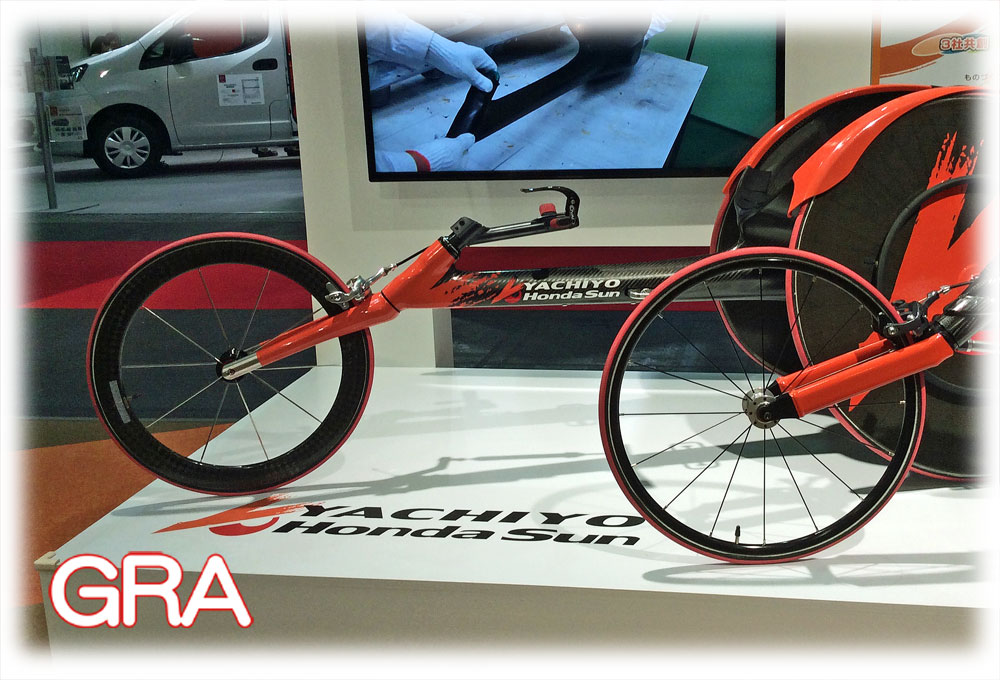

ご存知の通り、車椅子の進行方向の調整は手で駆動する左右の後輪への入力の調整で行ないます。ただ、競技トラックやマラソンコースの様に、比較的単純なコースレイアウトの場合は、後輪から遠く離れた位置に前輪を配置して、そのホイールベースの長さによって車体の直進安定性を高めて、選手は全力で後輪を駆動できる様に配慮された設計になっています。そして、画像の通り、とても大きなキャスター角になっている事が一般的です。 これは、一見、選手が操舵ハンドルを操作しやすい為になっていると思われがちですが、それとは別な狙いがある事が分かります。それは、旋回を効率良く行なう為だと考えられます。つまり、キャスター角が大きい程に、同じ操舵角であっても、旋回に及ぼす力が大きくなるのです。その結果、小さな操舵角であっても、効果的に旋回が行なえるのです。しかし、大きなキャスター角には弊害もあります。それは、例え直進中であっても、路面の影響や駆動力の不均等などによって、常に左右どちらかに旋回を始めてしまう事です。だから、この弊害への対策として、トラックレーサーの前輪操舵部には強力なダンパーやスプリングを装着されていて、常に直進方向を保つ仕組みになっているのです。そして、旋回の際には、操舵ハンドルで操舵すると、自動的にその位置で操舵角が固定され、直進に戻った際には、操舵ハンドルで固定を解除すれば、ダンパーとスプリングの働きで直進状態に戻る仕組みになっています。更に、この仕組みがトラックレーサーで有効な理由は、前輪荷重の少なさです。キャスター角が大きな車両の場合、前輪(操舵輪)を操舵すると、車体の重さで操舵輪側の車体が下がります。そして、操舵で直進状態に戻す際には、その下がった車体を上げる力も必要になり、前輪荷重が大きな車両では大きな力が必要になる弊害があります。しかし、トラックレーサーの場合は、基本的に全り荷重は小さく、選手の操作で充分に対応可能になっている筈です。また、旋回時の操舵角の固定は、車体や選手の特性、或いは、走行レーンなどによって細かく調整可能になっていると推測できます。これで、パラリンピック観戦の楽しみが一つ増えます。
As an aside, I will introduce an example where the caster angle is set abnormally large. It is a wheelchair called a track racer, which is used in track events and marathons.
As you know, the direction of the wheelchair is adjusted by adjusting the input to the left and right rear wheels, which are driven by hand. However, in the case of relatively simple course layouts such as competition tracks and marathon courses, the front wheels are placed far away from the rear wheels, and the length of the wheelbase increases the straight-line stability of the body, so that the athlete can drive the rear wheels with all their might. And as you can see in the image, it generally has a very large caster angle. At first glance, this may seem to be to make it easier for the athlete to operate the steering wheel, but it turns out that there is a different purpose. It is thought to be to make turns more efficient. In other words, the larger the caster angle, the greater the force exerted on the turn, even with the same steering angle. As a result, even with a small steering angle, the turn can be made effectively. However, a large caster angle also has a disadvantage. That is, even when going straight, the wheel will always start turning to the left or right due to the influence of the road surface or uneven driving force. Therefore, to counter this problem, the front wheel steering of track racers is equipped with powerful dampers and springs, which are designed to keep the car moving in a straight line at all times. When turning, the steering wheel is used to steer, and the steering angle is automatically fixed at that position. When the car returns to a straight line, the steering wheel is released, and the dampers and springs return the car to a straight line. Another reason why this mechanism is effective on track racers is the small front wheel load. In the case of a vehicle with a large caster angle, when the front wheel (steering wheel) is steered, the weight of the vehicle lowers the body on the steering wheel side. Then, when steering to return the car to a straight line, a force is required to lift the lowered body, and a vehicle with a large front wheel load has the disadvantage of requiring a large force. However, in the case of track racers, the front wheel load is basically small, and the driver's operation should be able to handle it sufficiently, so it is not considered to be a big problem.
 ページ中の画像は クリエイティブ・コモンズ 表示 - 非営利 - 改変禁止 4.0 国際 ライセンスの下に提供されています 文章等は許可無く転載することを禁じます / Copyright GRA All Rights Reserved. |