Soumya Raychaudhuri, Patrick D.Sutphin, Jeffrey T.Chang, Russ B.Altman.
Basic microarray analysis: Grouping and feature reduction.
TRENDS in Biotechnology,19(5):189-193. 2001
[PDF]
・マイクロアレイデータ解析法の概論。クラス分けと遺伝子抽出について。
・データ:Lymphoma specimens, 47サンプル, 4026遺伝子 [Alizadeh]
・解析法
1.Unsupervised grouping : clustering → K-means clustering method with a Euclidean distance metric
2.Supervised grouping : classification → Linear discriminant analysis that uses differential weights to specify the features
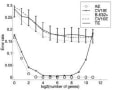
3.Unsupervised dimensional reduction : pruning uninformative features → PCA [図]
4.Supervised dimensional reduction : feature selection → Iterative LDA method
・使用ソフト:CLEAVER http://classify.stanford.edu/
・概要「We briefly review supervised and unsupervised methods for grouping and reducing data in the context of a publicity available suite of tools called CLEAVER, and illustrate their application on a representative data set collected to study lymphoma.」
・「When grouping is supervised it is called 'classification' and when it is unsupervised it is 'clustering'.」
・問題点「Unsupervised approaches can find novel profile groupings but are not designed to reliably produce groupings that are known from independent sources of information.」
・問題点「Features are removed because they do not provide significant incremental information and because they can confuse the analysis or make it unnecessarily complex.」
Basic microarray analysis: Grouping and feature reduction.
TRENDS in Biotechnology,19(5):189-193. 2001
[PDF]
・マイクロアレイデータ解析法の概論。クラス分けと遺伝子抽出について。
・データ:Lymphoma specimens, 47サンプル, 4026遺伝子 [Alizadeh]
・解析法
1.Unsupervised grouping : clustering → K-means clustering method with a Euclidean distance metric
2.Supervised grouping : classification → Linear discriminant analysis that uses differential weights to specify the features
3.Unsupervised dimensional reduction : pruning uninformative features → PCA [図]
4.Supervised dimensional reduction : feature selection → Iterative LDA method
・使用ソフト:CLEAVER http://classify.stanford.edu/
・概要「We briefly review supervised and unsupervised methods for grouping and reducing data in the context of a publicity available suite of tools called CLEAVER, and illustrate their application on a representative data set collected to study lymphoma.」
・「When grouping is supervised it is called 'classification' and when it is unsupervised it is 'clustering'.」
・問題点「Unsupervised approaches can find novel profile groupings but are not designed to reliably produce groupings that are known from independent sources of information.」
・問題点「Features are removed because they do not provide significant incremental information and because they can confuse the analysis or make it unnecessarily complex.」