Conditional precipitation probability model for a given time interval
Hydrostatistics is a discipline that aims to determine the extreme values of unit-time rainfall using probability statistics and apply them to water resource planning and the design and management of hydraulic structures. Conventional hydrostatistics directly analyzes the extreme values of unit-time rainfall, assuming that unit-time rainfall is an independent random variable. However, this assumption is only partially valid, and experiencing unprecedented extreme values can lead to damages beyond expectations.
One possible explanation for the emergence of unprecedented extreme values is the presumed influence of global warming. Therefore, there is a need to develop new probabilistic models for studying the extreme values of unit-time rainfall.
Interestingly, such new probabilistic models already exist in the form of analytical models known as the Depth-Duration (DD) and Depth-Area (DA) equations. Notable examples of the DD equation include the Sherman equation, and the Horton equation is a well-known example of the DA equation.
Sherman式: rt = a / t^c, where, rt is average rainfall intensity at time t, and a and c are coefficients.
Horton式: PA = P0 * exp(-k * A^n), where, PA is average rainfall over area A, P0 is maximum rainfall within area A, k and n are coefficients.
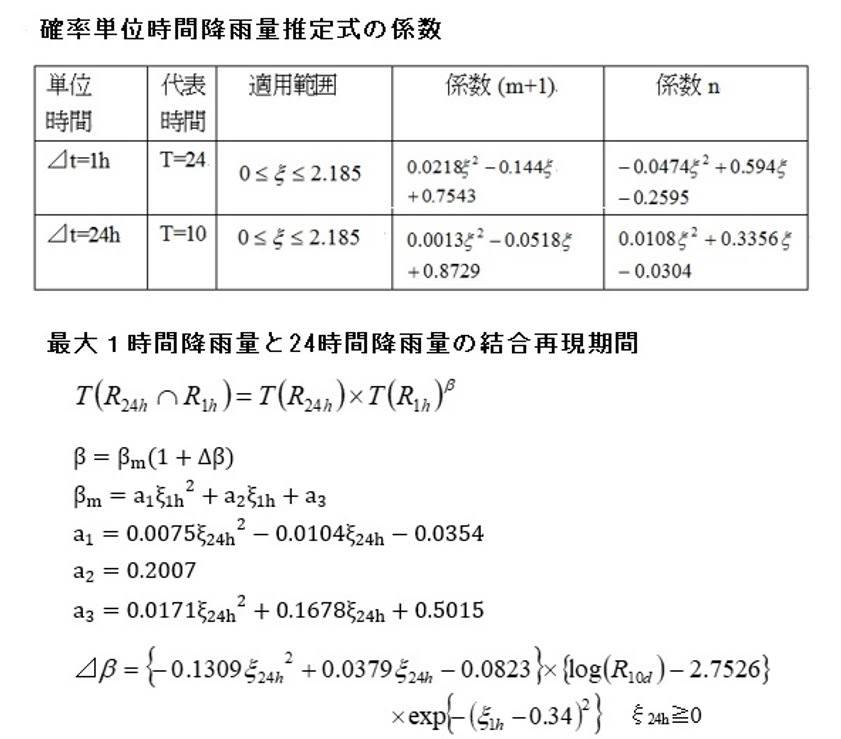
Analysis of the DD equation is typically conducted on log-log paper. The coefficient c is known as the shape parameter. This designation stems from the observation that on log-log paper, the mean rainfall intensity over time t exhibits an approximately linear distribution with respect to the time axis.
However, as long as the coefficient c is referred to as the shape parameter, the DD equation does not qualify as a probabilistic model. To transform the DD equation into a probabilistic model, dimensionless unit time 1 and dimensionless representative time T are introduced. The rainfall intensity per unit time is represented by r1, and the average rainfall intensity over time T is denoted by rT. The DD equation is expressed as the ratio between these two quantities.
Log(r1/rT)=logT^c
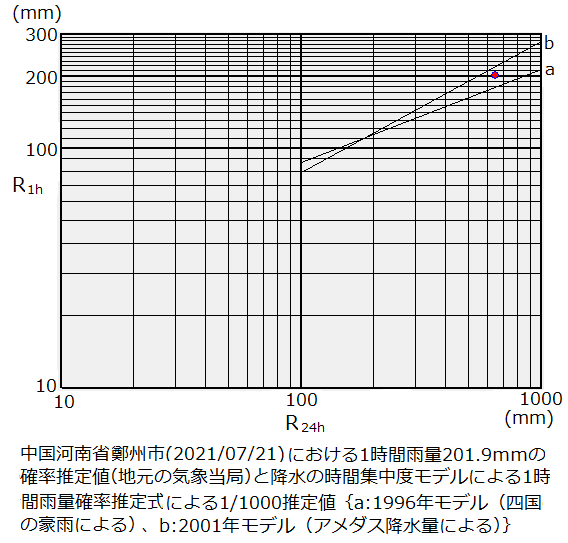
Consider a scenario where T units of time receive RT mm of rainfall. What is the maximum possible rainfall in millimeters per unit time? The maximum value is RT/1, and the minimum value is RT/T. In the former case, the coefficient c is equal to 1, while in the latter case, c is equal to 0. Consequently, the coefficient c is distributed within the range [0, 1]. However, if RT is sufficiently large, the distribution becomes (0, 1). This implies that the coefficient c can be transformed into a random variable.
By incorporating dimensionless unit time and dimensionless representative time into the solution of the DD equation, the DD equation can be transformed into a probabilistic model. However, while the coefficient c is determined by a random variable, it is also dependent on RT over time T. Therefore, unit-time rainfall is not an independent random variable. I refer to the coefficient c as the "temporal concentration degree of rainfall."