Fiber optic loopback is also known as fiber optic loopback cable or fiber optic loopback module. It is designed to provide a media of return patch for a fiber optic signal, offering a generous yet manageable fiber loop virtually eliminating bend loss, and commonly used for fiber optic testing applications or network restorations. It can also utilized to diagnose the problems of optical networking equipment. Sending a loopback test to network equipment, one at a time, is a technique for isolating a problem. Fiber optic loopbacks is compliant with Fast Ethernet, Fibre Channel, ATM and Gigabit Ethernet, etc.
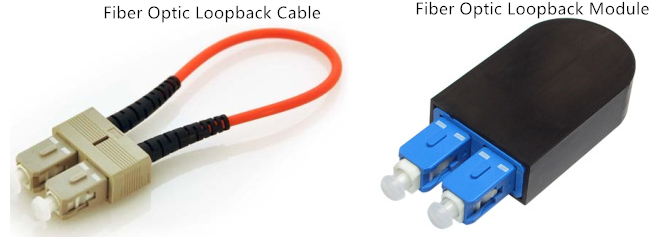
Fiber optic loopbacks can be with different jacket types, cable diameters, connector terminations and cable lengths. Traditional fiber optic loopbacks, namely fiber optic loopback cables, can be regarded to be two fiber optic connectors on the same piece of simplex fiber jumpers put together, thus it forms a loop. Classified by the connector types, the most common two types of fiber optic loopback cables are SC and LC type, besides there are also FC, MTRJ, and MTP types.
In addition to the traditional fiber optic loopbacks, there are also molded fiber optic loopbacks (or fiber optic loopback plugs), i.e. fiber optic loopback modules, with compact design. Unlike the traditional fiber optic loopback cables with visible cable parts, fiber optic loopback module has its cables and fibers well protected inside the housing. It integrates every part into one single body, which help save space and make it easier to operate as well as offer better protection to the whole product. By incorporating a rigid connector shell for fiber protection with an easy to use, ergonomic package, the fiber optic loopback module is designed for durability and performance. Molded fiber optic loopbacks are also mainly available in SC and LC types, which are easy to use for fiber optic test purpose in the lab experiments or manufacturing environment.
Just like fiber optic patch cables, fiber optic loopbacks can also be classified by fiber types: single-mode and multimode. The fiber types can be 9/125µm single-mode fiber, 50/125µm multimode fiber, or 62.5/125µm multimode fiber. Typically single mode SC and LC loopbacks are blue, and typical multimode LC and SC loopbacks are beige. The color also goes with the practice of SC LC fiber patch cable.
A tipical application of fiber optic loopback is to check fiber optic transceiver by loopback test. Loopback test means a hardware or software method, a loopback test, feeds a received signal or data back to the sender. It is utilized as an aid in debugging physical connection problems.
Loopback test is the easiest way to ensure the transceiver is working faultlessly. On fiber optic transceiver manufacturing floors and in R&D labs, a fiber optic loopback is used to verify the transceiver whether it is working perfectly as designed. Basically what the loopback does is directly routing the laser signal from the transmitter port back to the receiver port. Then the transmitted pattern is compared with the received pattern to make sure they are identical and have no error.
Fiber optic loopbacks feature single-mode and multimode loopback plugs designed for equipment testing, self-testing, engineering, network diagnostics and measurement applications. They play an important role in troubleshooting in laboratories and manufacturing environments. A high optical performance is achieved due to precision ceramic ferrule. The fiber optic loopbacks are precision terminated and feature extremely low loss characteristics for transparent operation in the test environment and in form of cable and module types.














