Ethernet cables or networks cables are used for data transmission between devices on a network. They consist of a copper cable with 4 pairs of wires and connected by RJ45 connectors on each end of the cable. Most Ethernet cables in use today are either Cat5e and Cat6 which offer higher data transfer rates than the older types such as Cat5 and Cat4. Although various types of Ethernet cables look the same, the internal wiring distinguishes. Ethernet cables can come in two different wiring applications: straight-through and crossover, each of them with different wire arrangement in the cable for serving different purposes.
Straight-through cable is the most common type and is used to connect different type of devices. This type of cable is easy to find in stores and can be used to: 1)Connect a computer to a switch/hub's normal port.
2)Connect a computer to a cable/DSL modem's LAN port.
3) Connect a router's WAN port to a cable/DSL modem's LAN port.
4) Connect a router's LAN port to a switch/hub's uplink port. (normally used for expanding network)
5) Connect 2 switches/hubs with one of the switch/hub using an uplink port and the other one using normal port.
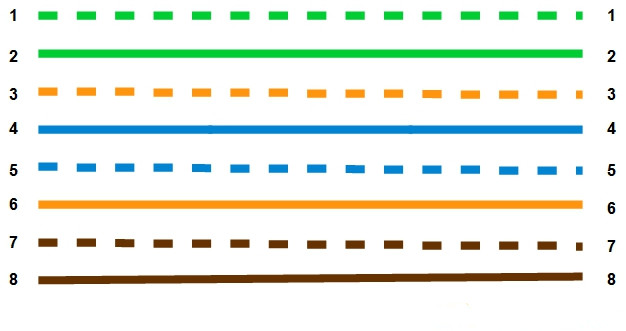
If you need to check how straight-through cable looks like, it's easy. Both side (side A and side B) of cable have wire arrangement with same color. For example, Cat5e UTP cable usually uses only four wires when sending and receiving information on the network. The four wires, which are used, are wires 1, 2, 3, and 6. When you configure the wire for the same pin at either end of the cable, this is known as a straight-through cable.
Crossover cables are usually used to connect the same type of devices and may be a little harder to find since they aren’t used nearly as much as straight-through cables. A crossover cable can be used to: 1) Connect 2 computers directly.
2) Connect a router's LAN port to a switch/hub's normal port. (normally used for expanding network).
3) Connect 2 switches/hubs by using normal port in both switches/hubs.
Compared with straight-through Ethernet cables, the internal wiring of crossover cables reverses the transmit and receive signals. That is to say, the two end of the crossover Ethernet cable are wired differently. And the reversed color-coded wires can be seen through the RJ-45 connectors at each end of the cable.
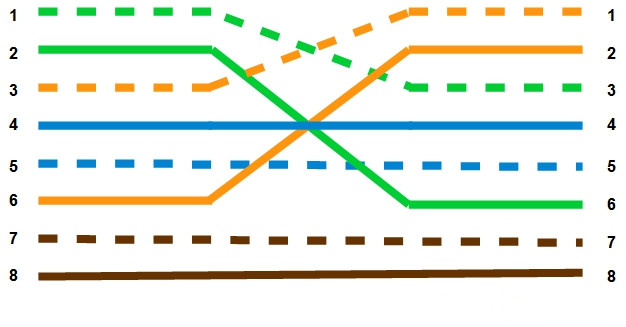
Whether they are straight-through or crossover cables, all Ethernet cables essentially look the same. When dealing with the inevitable pile of unlabeled cables that forms in every home, this can make dealing with them tricky. Fortunately, you can quickly identify crossover and straight cables if you know what to look for.
When determining if an Ethernet cable is a straight or crossover cable, examine the connectors. Observe the pin configuration carefully. The pins are color coded, so you should have no trouble doing this. If the pins are configured in the same way, you are looking at a straight cable. If not, it is a crossover cable.
Nowadays, the need for crossover cables has been eliminated with more modern equipment. Gigabit Ethernet was created with a widely used option called Auto-MDIX (automatic medium-dependent interface crossover). This technology detects whether you need a crossover cable or a straight-through cable, and it automatically configures the network interface card accordingly, which means that crossover function would be enabled automatically when it's needed.










※コメント投稿者のブログIDはブログ作成者のみに通知されます