
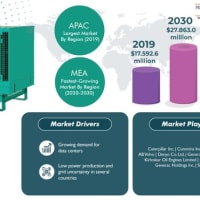
The improving economy has led to a high demand for products, which in turn, has given a major boost to industries across the world. There is a common perception that cities offer better standards of living, which has resulted in rapid urbanization. Therefore, growing cities and towns and the establishment of new industries at a large scale have contributed hugely in the demand for electricity. To meet such high demand, different energy-generating utilities are being tried, tested, and deployed, including the concentrated solar power plant (CSP). At the global level, the highest demand for CSPs was generated from the Asia-Pacific (APAC) region, and the National Energy Administration of China reported that nearly 111 CSP projects with a cumulative capacity of 9 GW were underway. Similarly, in India, two projects with a total capacity of 225 MW are being installed in the states of Gujarat and Rajasthan. Further, thermal energy storage systems are being popularized by governments in order to help reduce load on power grids.
Get free sample copy of thermal energy storage market overview at: http://bit.ly/2Cy12wW
Thermal energy storage systems store the excess energy produced and help in filling the gap generated during the peak demand. They are of the following types: pumped heat electrical (PHES), concentrated solar power, and ice thermal energy, and chilled water thermal energy. During 2013–2017, CSPs were installed the most globally. Countries such as the U.A.E., Morocco, and Australia have been greatly deploying the advanced CSP systems. These systems make use of mirrors for concentrating sunlight and converting it into high-temperature heat. This heat is then used for creating steam for driving a turbine for generating electricity. A CSP plant contains two parts, first, which collects the solar energy and converts it into heat, and the second, which converts the heat energy into electricity. In the coming time, the fastest growth in demand is expected to be witnessed by the PHES systems. The thermal energy storage market is predicted to register a 15.9% value CAGR in the coming years.
Thermal energy storage systems are based on these technologies, namely sensible heat, thermo-chemical, and, latent heat. The sensible heat storage technology makes use of the changing temperature of the material and its heat capacity that occurs during charging or discharging. A variety of storage media are used, ranging from earth, sand, to clay and rock; the most common storage media is water. This technology is most commonly employed in hot water tanks. Its highest adoption can be attributed to its discharging and charging of heat for umpteen number of cycles in a storage system. In the coming time, latent heat-based thermal energy storage systems are expected to register the fastest growth in demand.
The surging demand for electricity has put an immense burden on all conventional sources of energy-generation. Therefore, alternatives are being found for generating electricity and storing it for times when the demand is not being met or in the case of a grid failure. The new technology is the underground thermal energy storage (UTES) system. In regions, such as North America and Europe that have a high presence of salt caverns and aquifers, heavily deploy these systems. This technology is extensively used for power generation and underground thermal energy storage. Thus, increasing focus on the UTES technology can help manufacturers widen their customer base by offering the new technology to consumers.
Get free sample copy of thermal energy storage market overview at: http://bit.ly/2Cy12wW
Thermal energy storage systems store the excess energy produced and help in filling the gap generated during the peak demand. They are of the following types: pumped heat electrical (PHES), concentrated solar power, and ice thermal energy, and chilled water thermal energy. During 2013–2017, CSPs were installed the most globally. Countries such as the U.A.E., Morocco, and Australia have been greatly deploying the advanced CSP systems. These systems make use of mirrors for concentrating sunlight and converting it into high-temperature heat. This heat is then used for creating steam for driving a turbine for generating electricity. A CSP plant contains two parts, first, which collects the solar energy and converts it into heat, and the second, which converts the heat energy into electricity. In the coming time, the fastest growth in demand is expected to be witnessed by the PHES systems. The thermal energy storage market is predicted to register a 15.9% value CAGR in the coming years.
Thermal energy storage systems are based on these technologies, namely sensible heat, thermo-chemical, and, latent heat. The sensible heat storage technology makes use of the changing temperature of the material and its heat capacity that occurs during charging or discharging. A variety of storage media are used, ranging from earth, sand, to clay and rock; the most common storage media is water. This technology is most commonly employed in hot water tanks. Its highest adoption can be attributed to its discharging and charging of heat for umpteen number of cycles in a storage system. In the coming time, latent heat-based thermal energy storage systems are expected to register the fastest growth in demand.
The surging demand for electricity has put an immense burden on all conventional sources of energy-generation. Therefore, alternatives are being found for generating electricity and storing it for times when the demand is not being met or in the case of a grid failure. The new technology is the underground thermal energy storage (UTES) system. In regions, such as North America and Europe that have a high presence of salt caverns and aquifers, heavily deploy these systems. This technology is extensively used for power generation and underground thermal energy storage. Thus, increasing focus on the UTES technology can help manufacturers widen their customer base by offering the new technology to consumers.



















※コメント投稿者のブログIDはブログ作成者のみに通知されます